Stay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
As we near the end of 2022 and the start of 2023, let’s look at three things in relation to the freight market: freight volumes, the rates, and what’s happening in the maritime segment.
SLOWING FREIGHT VOLUMES
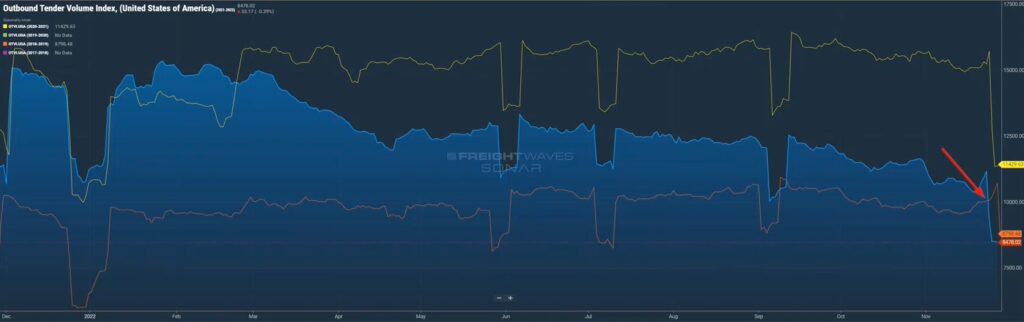
In Figure 1.1, you can see the contracted outbound tender volume index over the past four years. The yellow line on the top represents 2021, the blue line represents 2022.
Since about the end of the first quarter of this year, we started seeing those volumes pacing around the same way as last year, but then all of the sudden they started to take a nosedive. Contract volumes are down around 15 percent below 2021 levels. What that means is we’re seeing less volume trickling to the spot market and this trend will certainly continue as we go into 2023.
FALLING RATES
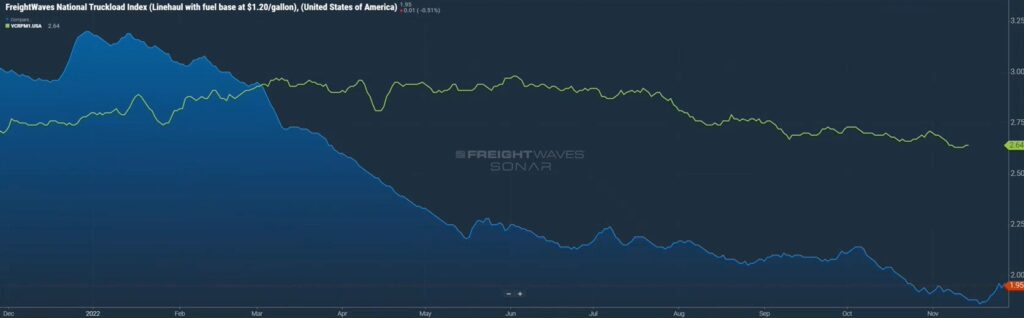
Speaking of rates, in figure 2.1, you’ll see the top green line represents the average van rate for contracted freight. The blue line is vans for the spot market.
As you can see, just like with freight volumes, they were running neck and neck until about March, and then there was a discrepancy. We’re seeing this on the rates side as well. Typically, the difference between contracted and spot rates is maybe 10 or 15 cents per mile. The fact that right now it’s about 70 to 80 cents a mile, we’ve never seen it at that high of a discrepancy. We do feel that as we get into the bidding season, new contracted rates will start to kick in, so we do anticipate that the green line will trend down. I’m not sure how much the blue line, the spot line, can continue to go, as it’s currently sitting at just below $2.00/mile. We may soon reach a point where carriers are not profitable on spot rates.
FINDING MARITIME BALANCE
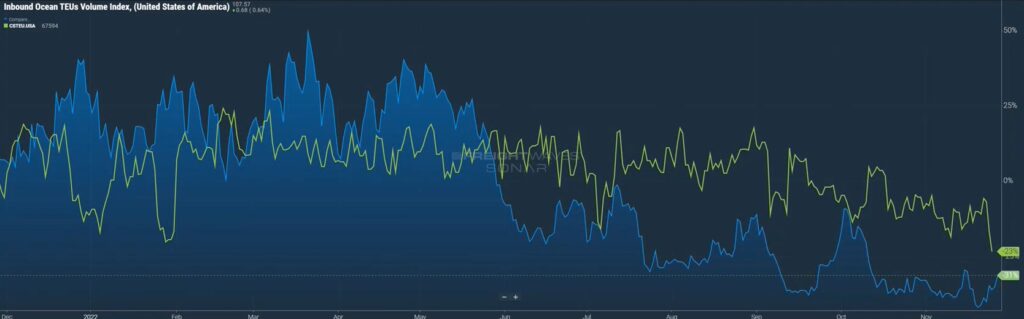
On the maritime side of things, in figure 3.1, the green line shows the number of actual containers that are clearing customs. They are coming off the ships, being unloaded, and clearing customs to be distributed via warehouses, intermodal, truckload, and what have you. The blue line shows the number of actual import bookings that have happened.
You may say to yourself, that doesn’t make sense. If somebody is booking freight and that number is going down, how come we are still clearing these containers? Remember, throughout much of 2021 and even 2020, there was a backlog of ships, particularly on the West Coast, waiting to get unloaded. So, while the flow of ships is not coming into the ports as greatly as it was, it just kind of shows you how big of a backlog there was, that it’s taken six months and we’re still not through this backlog of ships, both on the West and East Coast.
Overall import volume is down 20 percent year over year. Yet, East Coast and Gulf ports are up as shippers moved their freight to the East Coast when the West Coast was originally facing backlog delays.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Low, single-digit rejection rates on contracted freight mean less is hitting the spot market, by some accounts 30 percent less than last year.
Carriers need, and we need carriers, to remain solvent. Be diligent in negotiations with carriers but understand that we are very close to the floor for when a carrier becomes unprofitable.
Less freight is coming through the ports. Short-term will trigger an over-supply situation, particularly on ports with declining YoY volumes like Los Angeles and Long Beach. Other ports like Savannah, Houston, New York, and New Jersey will see more capacity balance.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive Weekly News Updates every Friday by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Join Our Mailing List for Frequent News Updates