Stay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
Shippers – Don’t wait ‘Til It’s Too Late
Probably every shipper has, at certain times or maybe all the time, been inundated with requests to handle their freight over the past year. This is in stark contrast to 2021 and most of 2022 when carriers and brokers were keenly focused on existing customers and not as aggressive in pursuing new business relationships.
Currently, shippers are enjoying relatively abundant capacity and spot rates, which have fallen below $2.00 per mile. As we all know, the freight market is cyclical. Several signs point to a period of supply and demand balance, and likely a crunch with capacity. Will it happen tomorrow? No. Six months from now? Possibly. Most likely, we’ll see this scenario play out as we head toward the latter part of 2024.
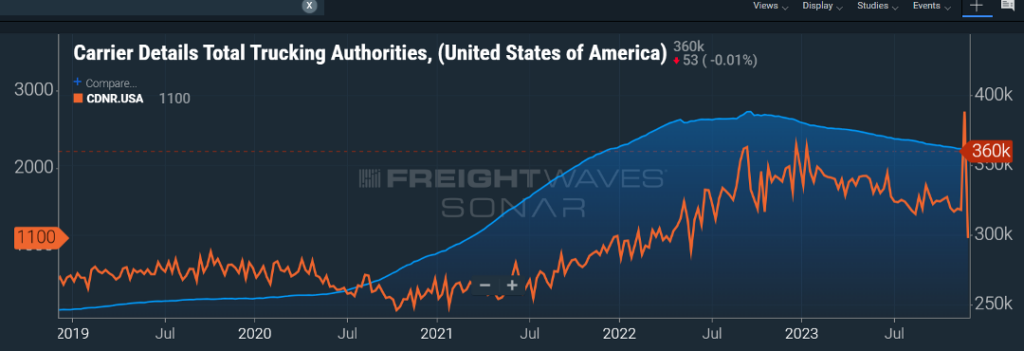
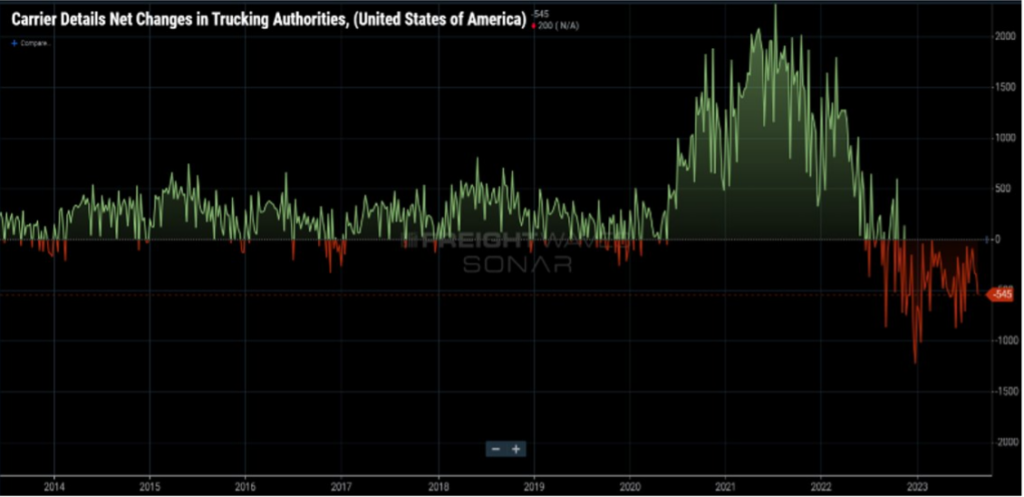
Figure 1.1 shows the total for-hire trucking authorities (blue line) and the carrier net revocations of authority (orange line) over the past five years. Clearly, carriers started flooding the market in late 2020, in response to the surge in goods moving within the supply chain. Much of that was consumer driven thanks to direct and indirect government stimulus action.
As we’ve seen freight volumes decline, carriers, mostly single person operations or small and micro fleets, have decided the juice is not worth the squeeze. This downward trend in available for-hire carriers will continue, and possibly accelerate, as we head toward more lean freight months ahead.
Shippers over the past year have right-sized their provider network. Now is the time for shippers to look at their volume forecasts and imagine having to manage that freight movement with 25-40 percent fewer providers than they currently have in their network.
If you haven’t started efforts to expand your carrier and broker partners, don’t wait until you have freight sitting on your dock and no one to move it from point A to point B. Nobody wants to be stymied like they were just a few years ago.
LTL Costs Rise
Does it feel like LTL shipments are getting more expensive, while truckload shipments are going the other direction? Why are the rates not cheaper if freight volumes are less than what we saw a few years ago?
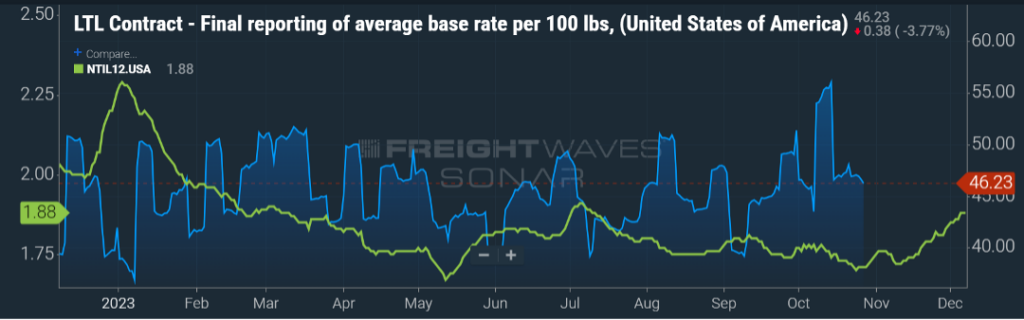
Figure 1.2 shows the spot truckload rate (green line) being almost $0.40 per mile less than the beginning of the year. LTL for the most part has seen rates (blue line) gradually head upwards as we have gone throughout the year.For a new shipper to the industry, this can be a head scratcher.
Short answer, truckload has a much more expansive network of providers, and as we highlighted above, that door being opened for new entrants into the market can happen quickly. The LTL model is more complex and a much bigger barrier of entry to the market. It would be a tremendous capital investment for a new LTL entrant to enter the market – trucks, trailers, terminals, labor, maintenance, etc. With the recent departure of one of the top 10 LTL providers (Yellow Corporation), that freight volume has been gobbled up by the remaining LTL carriers in the market but for the most part at a higher rate.
We are also approaching the time of year when LTL carriers, after assessing their financial statements and forecasting costs for the upcoming year, will start knocking on doors to discuss general rate increases (GRIs). Notice I said “increases”, not the other way. Don’t be surprised when your LTL contact lays out a proposal that elevates your LTL freight spend by four-to-six percent in the coming year.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
FLAT RATES, EXCEPT FOR LTL
Much of what we have seen this year has been around carrier rates remaining relatively flat. Apart from a few seasonal or holiday peaks, and a slight up or down influence due to fuel costs, spot rates and contract have been stagnant. As you can see in Figure 1.1, the green line has hovered between $1.70 and $1.80 for the past six months.
Less-than-truckload (LTL) rates, one would reason, would follow a similar pattern as they typically follow truckload rate movement with a few months lag. In the past few months, as indicated by the blue line in Figure 1.1, there has been an acceleration in LTL contract rates. As you probably recall, one of the larger LTL carriers, Yellow Corporation, filed for bankruptcy in August and ceased operations.
One may ask, “Well, why would rates elevate when the LTL industry was operating at less than capacity and nothing has caused an influx of new LTL freight?”
Yes, the remaining national and regional carriers were, based on available capacity on the books, able to absorb the freight Yellow was moving with no additional investment in equipment or labor. But just because the available resources are there, does not mean they are positioned in the places where service was needed.
This has necessitated LTL carriers realigning their network to move the freight that Yellow was doing prior. The more prevailing reason for rates to increase is the aggressive nature in which Yellow competed for the freight they were servicing. Typically, Yellow’s rates were far more discounted than most.
So, while the remaining LTL carriers in the network were able to position their fleets to handle the volume, they did not offer the same discounted rates that Yellow did. When you bundle all these factors together, you get rates increasing by about 10 percent in the last several months and I would not anticipate that 10 percent increase being reversed anytime soon. If anything, look for those annual general rate increases to happen as we embark on a new calendar year.
SUPPLY & DEMAND BALANCE IN 2025?
In prior monthly updates, we have highlighted the current freight environment being one of more supply than demand. Suffice to say that truckload freight volumes have been relatively unchanged over the last 12 months and carriers are saying “yes” to almost every shipment offered to them on the contract side.
This has resulted in less freight hitting the spot market and has helped to keep rates at levels that are $0.70-$0.80 less than contract rates. When will there be better balance? A great illustration of this from FTR in Figure 1.2 tells the story.
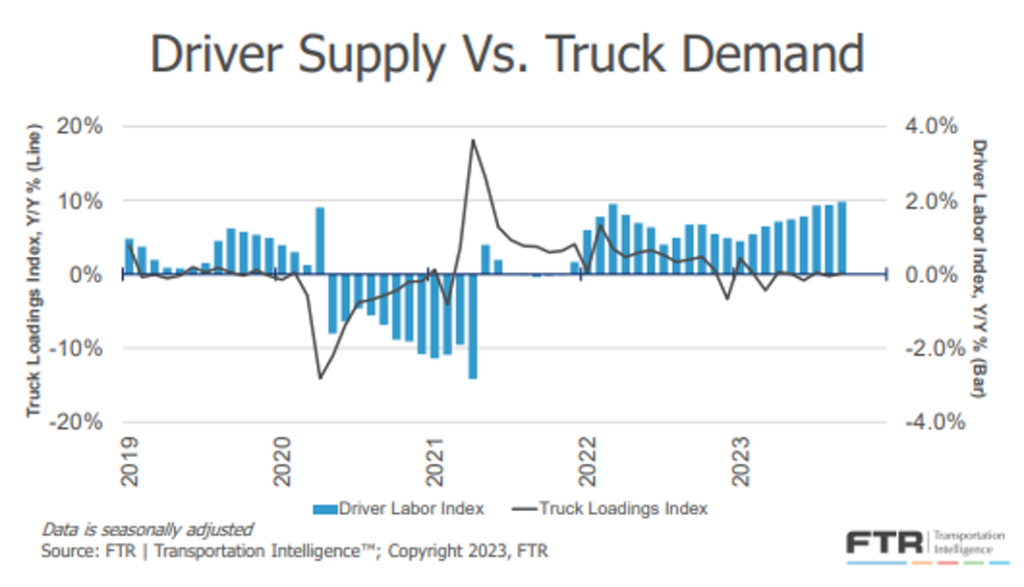
As you can see, the driver labor index sits well above the truck loadings index and has been for the past two years. When you factor in prospects for freight volumes to accelerate, economic conditions, and the pace at which carriers are exiting the market, it will most likely be 2025 before balance returns.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
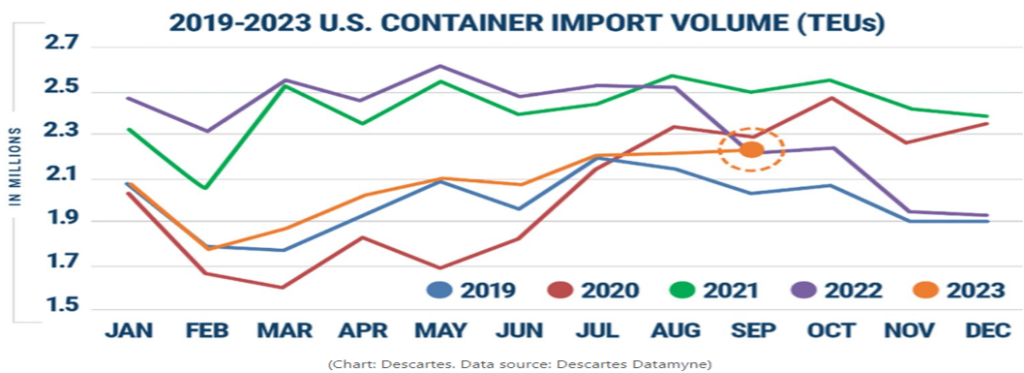
Imports on the Rebound?
For the past 14 months, much of the conversation around U.S. container import volume has been gloomy.
Figure 1.1 shows the steady decline in import volume that began in August of 2022, and those volumes have remained lower when you compare them year-over-year (YoY) for most of 2023.
September and October have begun to see that narrative change, with September of this year outpacing September of 2022. Comparing this year’s volume to 2021 and even 2022 is somewhat an “apples to oranges” comparison because of the frenzied consumer activity. A better comparison is how 2023 is stacking up versus pre-Covid years.
September 2019 saw approximately 2.05 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU’s) come through U.S. ports. September 2023 is seeing an increase of roughly seven percent in comparison. There are numerous efforts underway with U.S. retailers – like Walmart, Target and Amazon – to boost consumer sales with deals ahead of the traditional holiday buying season. This should continue to boost imports through the remainder of the year.
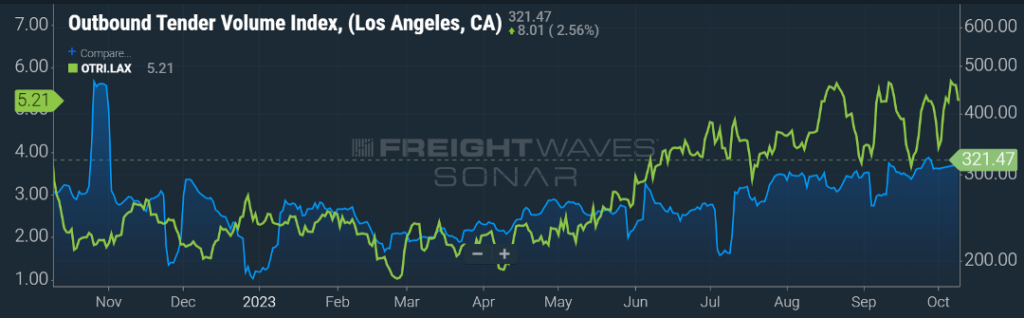
It will be important for shippers, carriers, and brokers to keep an eye on activity around U.S. ports as rates will reflect the supply and demand. An example can be seen the Los Angeles market. As seen in Figure 1.2, in the past 90 days, outbound volume from this market has increased almost 23 percent and the rate of carrier rejections has also shown an upward trend by over 50 percent.
Capacity Declining
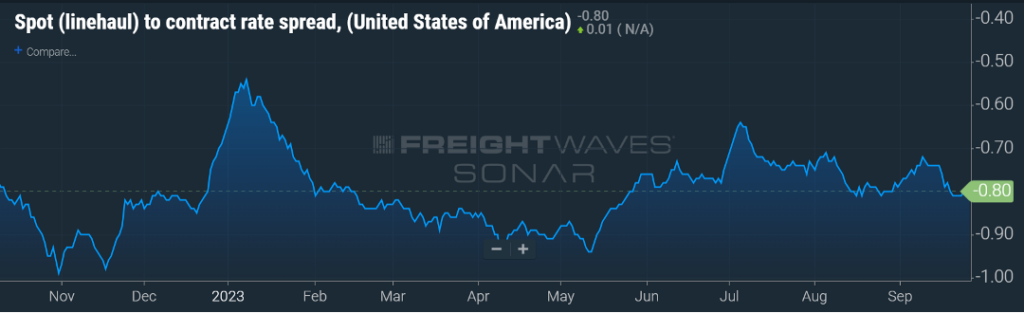
Six months ago, I would have taken a bet with anyone that the spread between contract and spot rates would not be greater than $0.50 per mile.
With capacity exiting the market and shippers making more frequent use of rate tools like mini-bids, the prevailing thought was that spot rates would remain relatively stagnant, or possibly a slight uptick, but contract rates would show a sharp decline. Good thing I was nowhere near a betting window.
The spread continues to hover around $0.80 per mile as seen in Figure 1.3, with contract rates being higher. Annual bid season is fast approaching, and it will be interesting to see if recent upward volume trends combined with an increase in carrier revocations will continue to keep contract rates where they currently reside or if the “sharpen the pencil” adage will be more prevalent.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
Freight Volumes Stagnant
As the U.S. continues to pull the levers to throttle the over-heated economy we experienced over the past few years, freight volumes, which are largely driven by consumer activity, have seen the impact of less buying from John and Jane Doe. It’s expected that muted consumer activity will continue through the first half of the calendar year 2024. We still expect to see a seasonal increase in spending at the end of the year for holiday shopping, but with consumers being more dependent on credit for purchases, and the rate of savings on the decline, expenditures are expected to be less than in prior years.
Combined with declines seen on the industrial production and manufacturing side, the hope for a rebound in freight volumes will not take place in 2023. The prevailing thought at this point is a return to a more balanced supply and demand regarding freight transportation will be driven by carrier attrition.
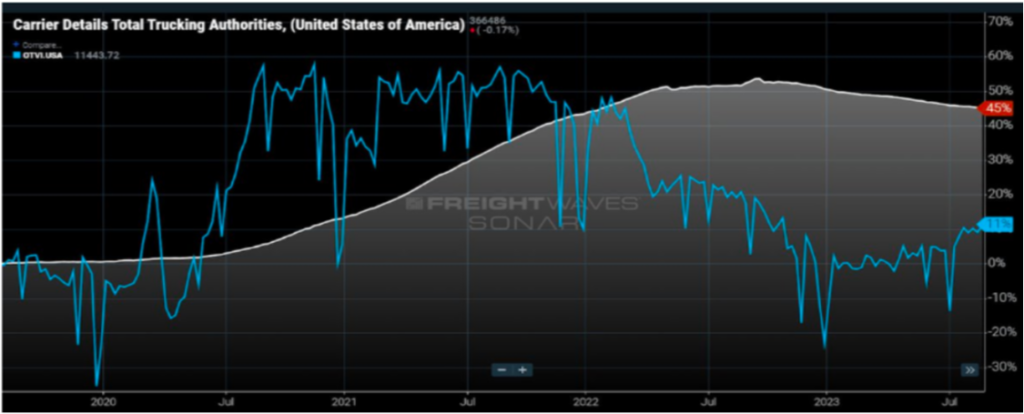
Nobody likes to see businesses fail, but we continue to see a market where oversupply has created trucking rates, particularly on the spot side, that are borderline if not less than what it costs a carrier to operate. Since the middle of 2022 and continuing this year, that decline in carriers for hire has continued as seen in Figure 1.1. Most of the attrition is carriers with five trucks or less, but as we’ve seen recently with Yellow Corporation closing its doors, no carrier is immune.
Capacity Declining
To further illustrate the impact of freight volumes on capacity, Figure 1.2 shows how capacity responds, almost in lockstep, with increases and decreases in freight volumes.
As freight volumes were accelerating in the latter part of 2020 and through early 2022, trucking companies popped up at a rapid pace to meet the demands of shippers. Carrier compliance, to a small extent, took a backseat as shippers were eager to make new friends with those who could get their product off the docks and to the end user in a race to satisfy consumer demand.
As freight volumes started to decline, as seen by the blue line in Figure 1.2, the need for capacity waned and began the downward trend (as shown by the white line) regarding carriers in the market.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
Length of Haul Does Impact Acceptance Rate
If you’ve been following the overall U.S. volume and shipment rejection rates this year, aside from the typical blips seen around the holidays, these have been relatively stagnant. The overall rejection rate has hovered very near the three percent range.
However, if you break that down by the length of haul, it’s clear that carriers clamor for those short-haul shipments, anything less than 250 miles, as this typically will allow the drivers to be home at night. On the other end of the spectrum, those mid-range shipments (250-450 miles) are seeing the highest rejection rate, just below four percent as seen in Figure 1.1.
There could be several reasons for this. Most likely it’s the fact that a driver can make a trip of that length in one day, but it’s not a full day’s worth of driving. So, if the driver is getting a per-mile rate and not driving for the full 11 hours that are eligible, this length of haul “loses” money when compared to longer shipments that allow the driver to hammer down for the full allotment of driving hours.
Now, I realize four versus two-point-five percent doesn’t seem like a big gap, but that is a 60 percent variance. If the freight volumes and capacity begin to balance, and rejection rates by length of haul follow the same trends, you could see mid-range rejection rates in the 15 percent range while shorter hauls only see rejection rates in the six percent range. Certainly that will have an influence on future rates.
SPOT AND CONTRACT GETTING CLOSER
As expected in Figure 1.2, the variance between contract and spot rates continues to shrink. Since the widest gap this year, when contract rates were about $0.78 per mile higher than spot rates, the gap has shrunk by almost 30 percent in a three-month period.
For the most part, spot rates have found a floor, and if anything, have seen a modest uptick. Contract rates have seen frequent requests for re-pricing. Carriers continue to refine their contracted rates balanced with the expectation of almost 100 percent compliance with freight tenders and excellent service.
In 2021 and 2022, shippers were open to expanding their carrier and broker pool as capacity constraints and increased volume necessitated more choices. Now that the balance has shifted, shippers are looking to right-size their partners, with a mix of compliance, price, and service steering their decision-making process.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive Weekly News Updates every Friday by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
Stagnant Freight volumes Continue to Push Carrier Compliance
2023 continues to see freight volumes showing little fluctuation. With freight volumes dipping more than 30 percent lower than the industry experienced over the past year, and little attrition at this point with carrier capacity, shippers are seeing freight tenders gobbled up almost exclusively as soon as they are offered.
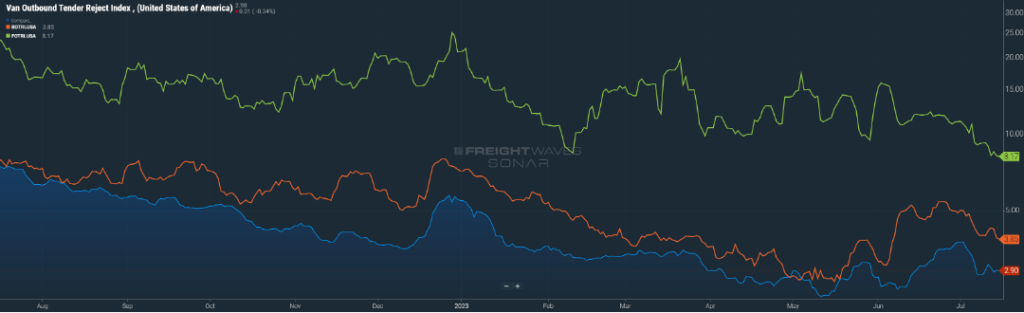
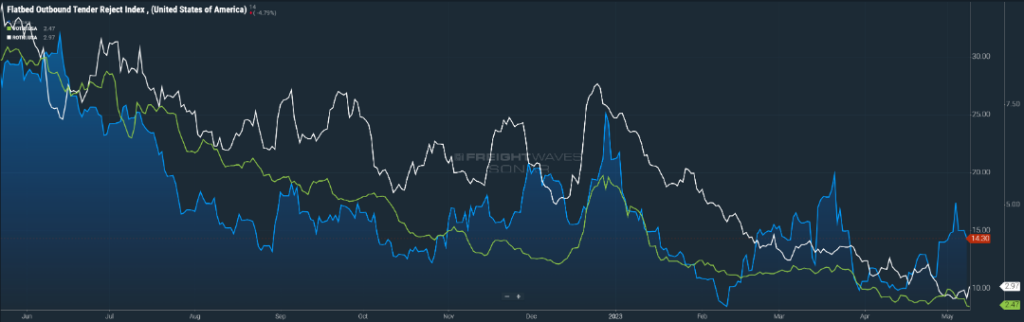
While there was a slight increase during the July 4th holiday week, primarily due to drivers taking extended time off the road, rejection rates have returned to their normal place of three percent on the van and reefer side (Figure 1.1). Flatbeds continue to see rejection rates almost three times what vans and reefers are experiencing, but the trend has been slightly downward over the past two months.
With no major signs of a rebound in volume, carriers will continue to strive for 100 percent compliance with freight tendered to them, and push for impeccable service to show why they need to continue to be a mainstay for shippers.

Start Preparing for a Balanced Market
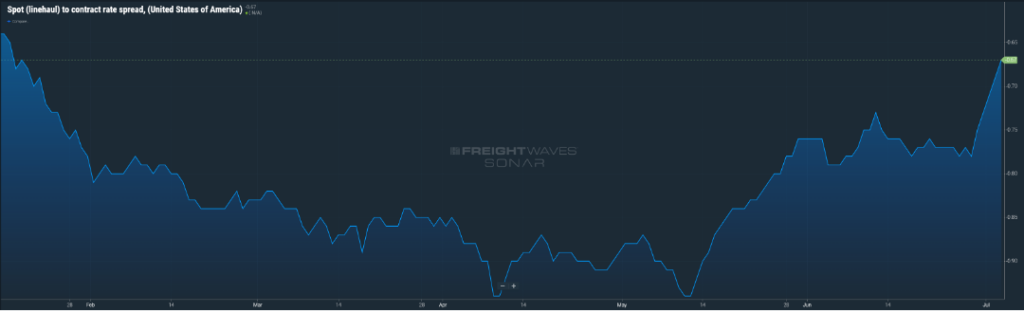
There seems to be a tightening of the gap between contract and spot rates (Figure 2.1). This was helped a bit by spot rates seeing an increase at the start of July, but contracted rates being rebid over the last three months have been the primary driver.
In a normal market, the spread between contract and spot rates is around $0.15 – $.20 per mile. Currently, contract rates are $0.65 per higher per mile.
As shippers expanded their carrier network in 2021 and 2022, look for a trimming over the next six months as shippers look to honor their volume commitments to contracted partners but provide themselves an opportunity to realize savings with capacity in the spot market.
We do expect the supply and demand cycle to balance as we head into 2024, so shippers need to ensure they are not creating hurt feelings with carriers that find themselves on the outside looking in. Remember, this industry is a three-legged stool, and everyone benefits when things are in balance.

Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive Weekly News Updates every Friday by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
Why are Contract Rates Elevated in Comparison to Spot Rates?
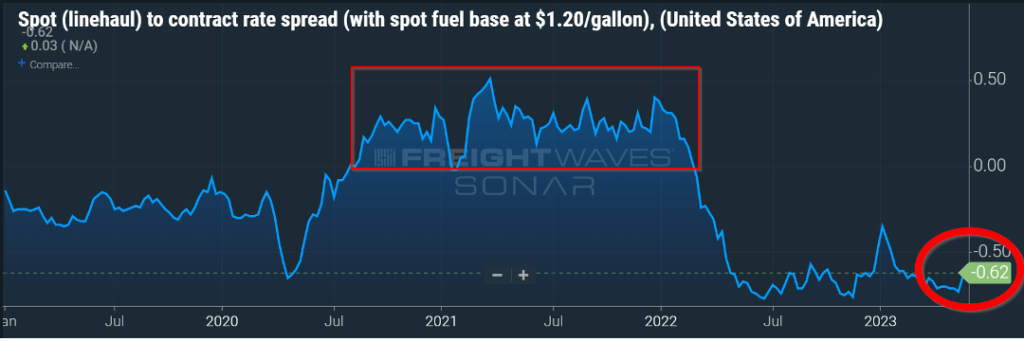
If freight volumes are, by some accounts, 30 percent less than what we experienced in the over-heated freight market of ’21 and most of ’22; and rejection rates are almost nil, why is the gap between contract and spot rates so wide, currently at $0.62 per mile as seen in Figure 1.1?
Typically, the gap between spot and contract in a “normal” freight market hovers around $0.15 per mile. During 2021 and most of 2022, spot rates were higher than contract rates for an extended period. For the majority of 2023, spot rates have fallen short of their contract rate counterparts.
As rates were high, especially on the spot side the last few years, capacity, particularly single-truck or small fleet operations, flooded the market. When challenging consumer conditions presented themselves towards the end of 2022, that meant less freight was traveling on America’s roads. So, you had a situation where less freight was in the contract space, which meant contract carriers were less likely to say “no” to freight tenders. This meant less freight flowed downstream to the spot market. When it did hit the spot market, there was a glut of carriers just waiting to bid for it, oftentimes doing so at break-even or very skinny profit margins just to keep the wheels turning.
We have seen in recent days the gap narrow. Part of that is due to continued pressure on contracted rates and another part of that is due to recent holiday and safety events that have stymied spot capacity. The gap will continue to narrow, mainly due to contract rates continuing to recede as spot rates, while maybe not at their floor, have very little room to move downward before they put carriers in a negative profit situation.
HO, HUM
On the topic of volumes and rejection rates, not much has changed since we last visited our trusty SONAR charts (Figure 2.1).
There was a brief blip in volume around the Memorial Day holiday, but that was short-lived, and volumes are returning to the levels we have become accustomed to over the past several months. Additionally, rejection of freight briefly pushed past the three percent mark but has since fallen back into the mid-two percent range.
Produce season will certainly give a boost to volumes, and drive rejections a tad higher. As well, depending on the situation with labor disputes at the west coast ports, that could potentially cause a brief halt to movement out of the west coast ports. When the labor disputes are resolved, it will give a burst to freight coming out of the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach especially. But for now, things are a bit ho-hum.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive Weekly News Updates every Friday by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
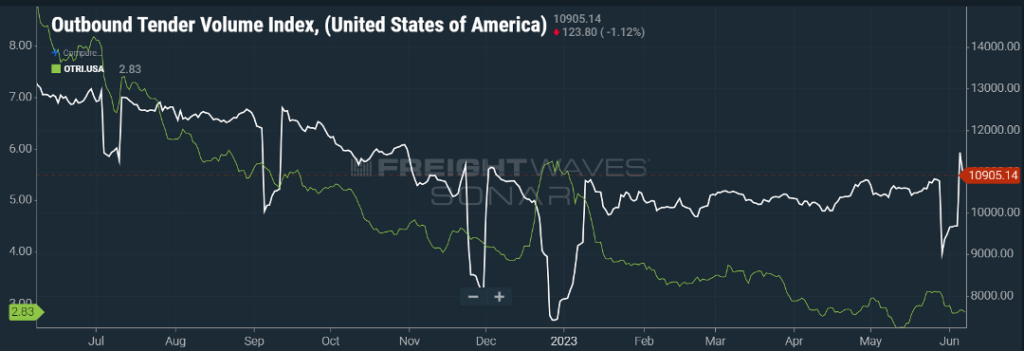
READY FOR A REBOUND?
Given the sluggish flow of freight in 2023, seeing any signs of life is encouraging. The industry muddled through the first four months of the year with the volume index registering very little movement as seen in Figure 1.1.
Heading into late April, and the early part of May, seeing upward movement was a welcome sight to carriers and intermediaries. Mid-spring typically brings a bounce from produce and seasonal freight, and this year we are seeing that lift, albeit not at an aggressive pace. Still, even with the slight upturn, freight opportunities continue to be gobbled up by carriers, particularly on the contract side. Historic low rejection rates of under three percent not only mean less freight heading to the spot market, but shippers continue to have the pendulum in their favor with regard to rates.
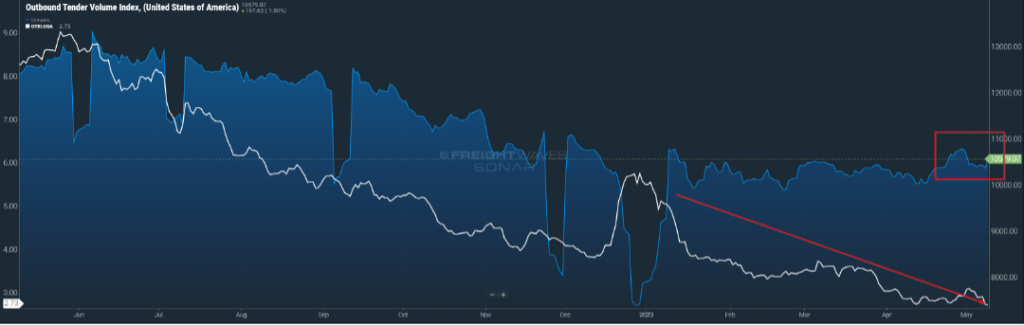
FLATBED SEES BALANCE
Speaking of tender rejection rates, the low rejection rate is not being felt across all types of equipment as we see in Figure 2.1.
Vans and reefers are pretty much accepting anything that comes their way. These are two equipment types that saw increases in their number from mid-2020 through 2022, primarily in response to the overwhelming consumer goods demand which typically travels in these types of trailers. Now that demand for these items has cooled, vans and reefers find themselves in a situation where demand is still there, just nowhere near what it was the past few years.
Flatbeds, on the other hand, did not experience the same demand. In the over-heated freight market, we experienced in the last few years, flatbeds felt the most normal with regard to freight patterns and demand. While they did not get the direct benefit of shippers clamoring for their services, flatbed carriers have also not experienced the same falling out. As a result, they enjoy a balanced market with rejection rates hovering in the mid-teens. This could be short-lived as downward trends in manufacturing and industrial production, combined with a cooling housing market, will lessen the demand for flatbed services.
the gap remains
Carrier rates continue to normalize.
As seen in Figure 3.1, the spot rate on the van side seems to have found a bottom. Contract rates have contracted slightly, but the spread between carrier-published rates and those available with spot rate pricing continues to push past $0.70 per mile. An uptick in spot rates may relieve some of the pressure from shippers on the contracted side for carriers. Ideally, a spread of $0.15-$0.20 would be more balanced.
Could this modest uptick in volume shrink the rate gap even more? Stay tuned to June’s update to find out.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive Weekly News Updates every Friday by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Join Our Mailing List for Frequent News Updates