Stay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
YES, IT IS IMPORT-ANT
There has been much buzz in the last month around inbound container volumes to U.S. ports. There are 300+ ports of entry for goods into the country, with much of that volume handled by the top 20. Most of that buzz is around the uptick in volume.
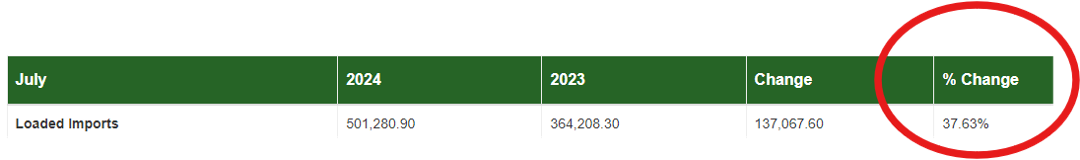
In figure 1.1, you will see for the port of Los Angeles, the largest in the country, that container volume is up almost 38 percent. That’s certainly impressive, but the neighboring port (Long Beach) was up a staggering 60 percent.
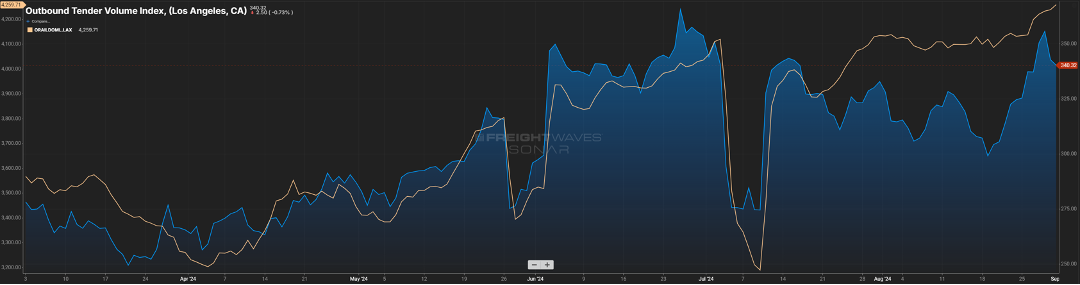
Many would anticipate this similarly impacting the outbound over-the-road volume for that market. And yes, while we see in Figure 1.2 via the blue line, there is a noticeable increase from what it was heading into the Memorial Day holiday, but it is not a direct correlation. The beige line represents the domestic rail volume from that same market, and unlike what we experienced in the “Covid years”, the rails have been a bigger mover of goods versus the bottlenecks we saw back then.
We should expect to see import volumes continue through the next few months. As goods produced overseas have become cheaper to buy, major retailers have taken advantage of these discounts with the anticipation of robust consumer spending. Remember, almost three-fourths of inbound volume is directly related to consumer purchasing. Good news for consumers as these retailers will want to liquidate this inventory quickly at lower prices.
NOT FAR FROM HEALTHY
While not in balance, the spread between contract and spot rates continues to shrink, now sitting about $0.60 per mile higher on the contract side. Keep in mind this gap was in the $0.75 to $0.90 for much of the past year. Almost in lockstep has been the tender rejection index. It has continued its slow upward movement as seen by the green line in Figure 2.1.
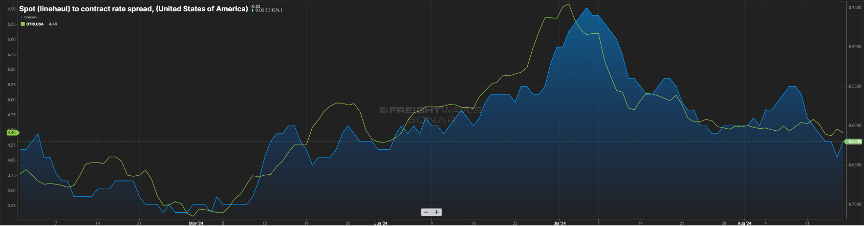
This can be attributed to capacity continuing to shrink slightly (Figure 2.2) and contract rates moving downward. It’s rare that spot rates will eclipse contract rates, but a spread of $0.40 to $0.50 is indicative of a healthier market, and we are not far from that right now.
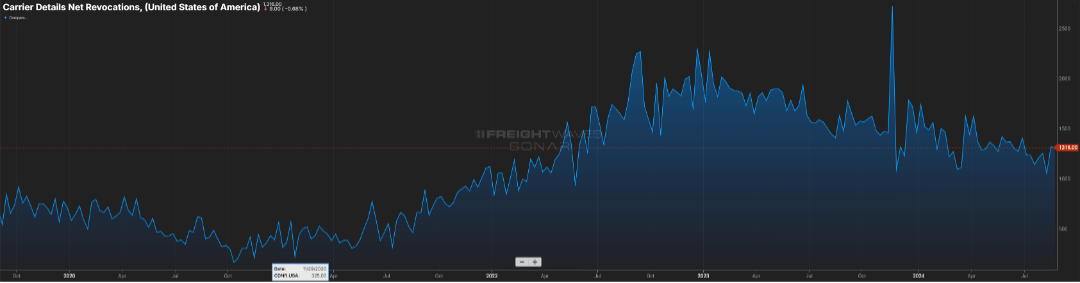
I spent a few days traversing the state of Tennessee recently. At one stretch of a major interstate, there was a back-up at least five miles long. Luckily for me, it was on the eastbound side, and I was heading the opposite direction.
What struck me was the sheer number of trucks that sat idled. By my estimates, almost 80 percent of the volume was truck traffic. And while you can’t tell if a van is loaded or not, every single flatbed had freight on it. So, ladies and gentlemen, freight is still moving in this country. While it may not feel like it, volumes are trending close to 2022 levels as seen in Figure 3.1 (blue vs. green line). They say the fourth quarter is the time when carriers make hay; so here’s to an optimistic outlook for the next four months.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
GOOD NEWS, BUT…
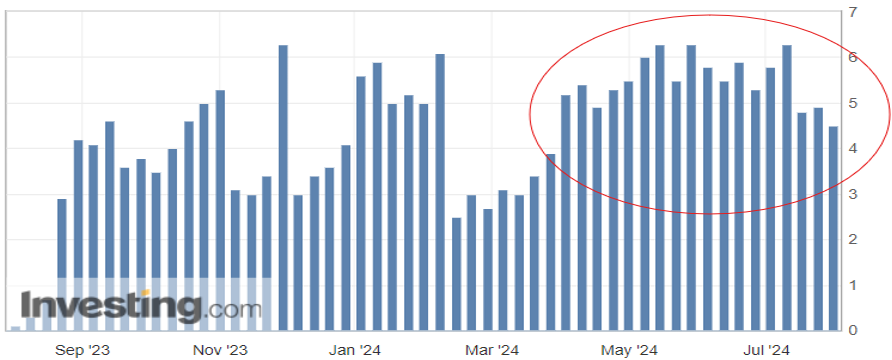
Consumer spending is the biggest driver of the U.S. economy, accounting for roughly two-thirds of the nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). One measurement of that consumer spending is the Redbook index, which compares year-over-year growth for large domestic general retailers (think Walmart, Amazon, Target). The index has averaged just over 3.5 percent for the past 20 years, so the recent year-over-year (YoY) growth in the four-plus percent range speaks to the strength of consumer spending (Figure 1.1). This index alone certainly gives reason for optimism, however there is a cautionary tale with regards to consumer debt.
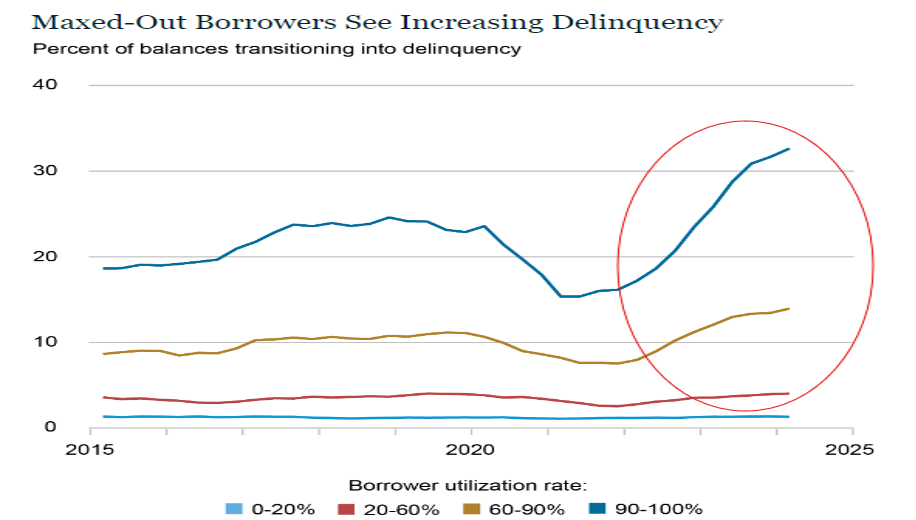
After years of next to zero interest rates to keep the economy on its legs, consumers have seen interest rates on the rise, with the federal funds rate at its highest level since the early 2000’s. With the increase in interest to borrow funds, combined with the increased costs of essentials (food, housing, energy), many households have turned to credit cards to fill the gap for funding of these necessities. Figure 1.2 from the New York Fed Consumer Credit Panel shows the rise in consumer delinquency particularly in those groups that utilize more than half of their available credit line.
While there appears to be relief on the horizon with the impending reduction in interest rates, it appears a portion of active consumers may be pulling back on purchases for those items that are not mission critical. This, in turn, will have an impact on restocking of inventories and trucking activity.
While it is not approaching the levels seen in 2021, the volume index is quickly approaching levels seen in 2022. This has buoyed optimism in the industry.
JUST SOME GOOD LUCK? TIME WILL TELL
The uptick in consumer spending, restocking of inventories and the threat of labor strife in the fourth quarter of this year has been to the benefit of those involved with the rail and import business.
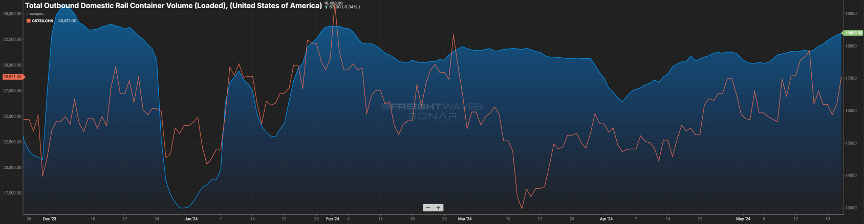
In Figure 2.1 below, the blue line represents loaded container rail volume in the U.S. and the past three months have seen the volume grow. Similarly, container volumes to the U.S. have been on the rise.
The orange line represents container volume from China over the past six months. While some of that traditional volume is now flowing through other countries, like Mexico, there is still a great deal of activity with U.S.-China trade. Will this continue or is it fool’s gold? That is something we will continue to keep an eye on as a pullback in consumer spending will dictate how the needle moves.
STAYING RIGHT WHERE WE ARE
Finally, looking at domestic over-the-road volume (blue line) compared with carrier rejection rates (green line). The slight upward trend continues with volumes and rejection rates (Figure 3.1). Rejection rates continue to inch towards 2022 levels, but a five-to-six rejection rate is about half of what one would see in a balanced freight market.
This has yet to manifest itself in the way of increased freight rates, as capacity still exists in the market.Shippers and carriers should anticipate little change in conditions (although hurricane season is looming) until early 2025.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
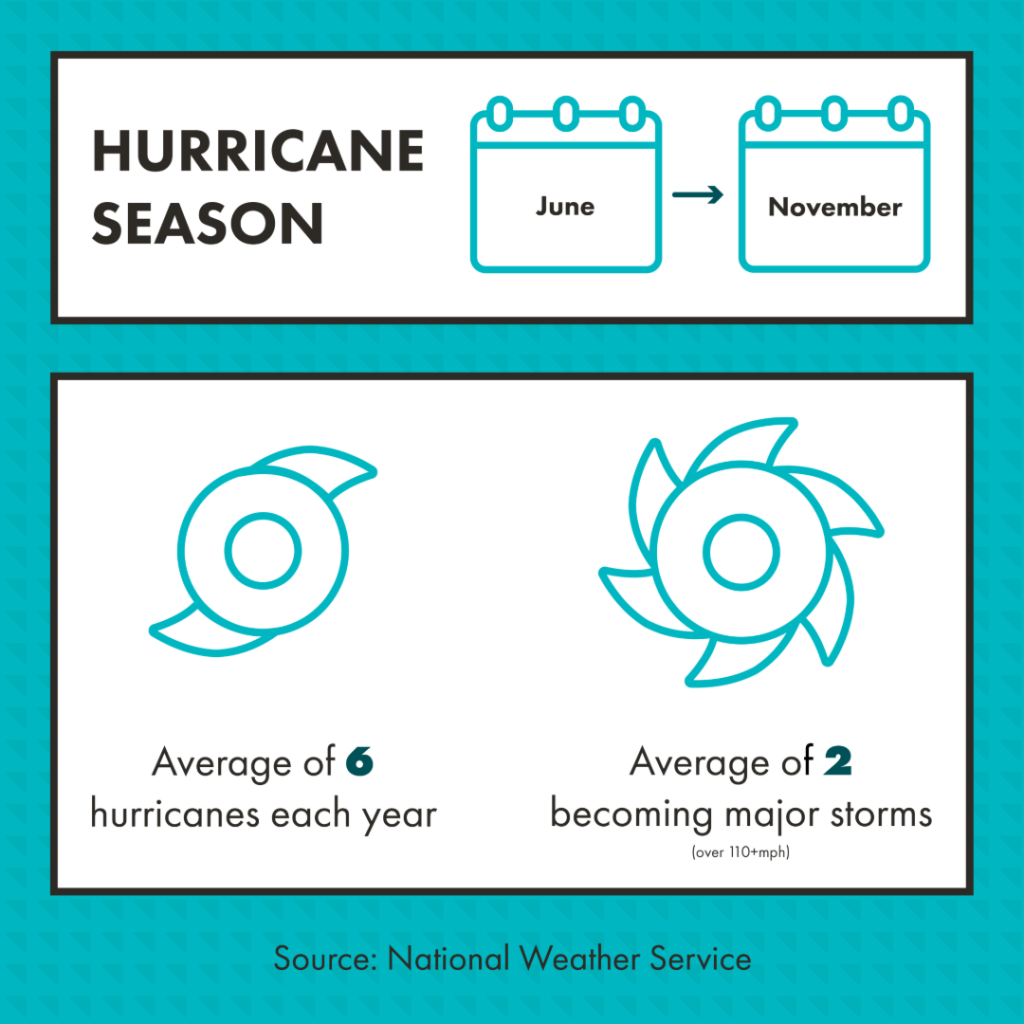
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxJune 1st through the end of November is considered Hurricane Season for the Atlantic and Gulf Coast, with heightened chances of storms occurring from early August to October. According to the National Weather Service, there’s an average of six hurricanes each year, with two typically becoming major storms hosting winds of 110-plus mph.
Even on its best days, the logistics industry is considered complicated. Throw a hurricane in the mix, and you can have straight-up chaos. Hurricane Season means supply chains should prepare for the worst in weather, like heavy rain, dangerous gusts of wind, limited visibility, and flooding. Shipping setbacks such as impassable roadways, stranded trucks and drivers, loss of cargo, and extended deliveries are just some of what can be experienced. Here’s what your organization needs to know to prepare during peak Hurricane Season so your company can avoid delays and a loss in revenue.
Supply Chain Tips for Peak Hurricane Season

Stay Informed
A hurricane’s path and level of impact can change very quickly. It’s crucial you stay informed of potential storms that could impact your supply chain during Hurricane Season.
Set up alerts to be notified of newly formed storms and hurricanes. When a potential storm is in your path find a trusted weather news source and check it often for updates. Don’t just follow the updates before the storm, but also during and after. You may also adopt and use advanced weather tracking systems to get up-to-date information to make informed, real-time decisions.
Maintain Communication

Natural disasters, like hurricanes, can have a huge impact on your company’s supply chain. An easy way to stay ahead is to be transparent and communicate openly throughout. Transparency builds trust and helps manage expectations during a crisis.
If a potential hurricane threatens your business, acknowledge it immediately. Then, start communicating with your customers and partners about the potential effects. Regular updates on potential disruptions and recovery efforts can go a long way in maintaining strong business relationships.
Have an Emergency Plan Ready
You should have a company-wide plan that outlines its actions during a hurricane. Your emergency plan should include important details like;
- an evacuation route for buildings affected
- a crisis communication plan
- assigned employee emergency roles and responsibilities
- instructions on how to protect inventory and equipment
- where emergency supplies are located and how best to use them
- how capable facilities will support when others are affected
When planning, make safety your company’s top priority during a hurricane. Once established, your plan should be reviewed often and updated as needed to ensure it remains effective. Additionally, running practice drills can help everyone know their roles and responsibilities.
Consider Alternatives

Consider what alternative workspaces and methods of transport you could use in the event of a hurricane. Are there temporary warehouse solutions where inventory could be stored? Could intermodal replace a truckload shipment that’s in the path of the storm? Are there alternative routes? How can facilities outside of the storm’s path support those affected? These alternative options should be included in your emergency plan.
While you may not have all the answers when planning, the more you include, the quicker you can make strategic decisions when needed. Having room for flexibility and adaptability is key to minimizing disruptions.
Have Visibility in Your Supply Chain

Visibility is needed now more than ever for supply chains. Having visibility not only helps you on good days but especially during hurricane season.
A transportation management system (TMS) can provide the necessary visibility during a hurricane. It provides critical data about your shipments and orders in real-time, giving you an advantage should a problem arise. This can help you make quick decisions to reroute shipments, avoid affected areas, and keep your customers informed.
See how a TMS could help youThink About Recovery

According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), almost 40 percent of businesses that have to shut down for 24 hours due to a natural disaster never open again.
Ensure your business won’t be in that 40 percent if it happens. Have a plan ready to roll for the aftermath of a hurricane. Prepare for the worst and then plan how to recover from it quickly. This will help prevent any potentially steep revenue loss.
Recovery Team, assemble! It’s time to identify the key employees and providers to get your business back to normal operations. An initial assessment will need to take place and your team’s sole responsibility should be to restore and resume processes. Having those alternative solutions and backup suppliers or providers will be handy here.
Weather the Storm with a Reliable Logistics Partner

Sometimes, you just need extra help. A relationship with a reliable logistics provider, like Trinity Logistics, can help your supply chain overcome the threats of Hurricane Season.
Hurricanes can roll in a cloudy overcast of unknowns, but Trinity shines a light toward safety and security. We have over 45 years of experience helping thousands of supply chains through ups and downs. We thrive on problem-solving and handling issues like the ones hurricanes can bring. We also have a dedicated After-Hours Team to support and quickly resolve any potential challenges – no matter the time of night, holidays, or weekend.
Our nationwide network of trusted carrier relationships ensures your shipments arrive safely at their delivery locations. Additionally, multiple transportation options offer the flexibility to keep your goods moving. Lastly, we’ll help you find real-time visibility with our customizable Managed Transportation solutions. Our dedicated Team (comprised of six Regional offices across the nation) is ready to help you maintain continuity and resilience in your supply chain.
Partner with Trinity logistics so your supply chain can stay afloat, no matter the weather. (Our exceptional service might just blow you away, though!)
GET A FREE QUOTE ON YOUR NEXT SHIPMENT SUBSCRIBE & STAY IN THE KNOW LEARN MORE ABOUT TRINITY LOGISTICS
Stay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
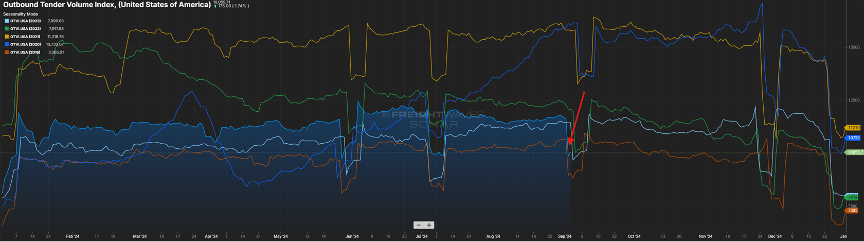
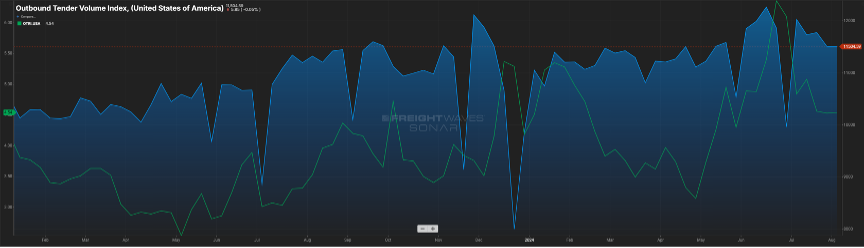
UP AND TO THE RIGHT
For the past year, the general direction of the Outbound Tender Volume Index (OTVI) has been on an upward trajectory as seen in Figure 1.1.
While it is not approaching the levels seen in 2021, the volume index is quickly approaching levels seen in 2022. This has buoyed optimism in the industry.
Another rise we’re keeping an eye on is the Outbound Tender Rejection Index, the rate at which carriers are saying “no” to freight where they have paper rates with a shipper. A six percent rejection rate may not sound important, but considering the rejection rate has stagnated in the three-to-four percent range for the past year plus, it’s another sign that the freight pendulum may be nearing more of a balanced market.
In 2021, rejection rates hovered in the 20-30 percent range. This was more a product of increased freight volumes and carriers realizing they could get higher rates in the spot market versus the contracted rates they had in place. The uptick in rejection now appears to be more of a limit of capacity in certain markets versus carriers hedging their bets on the open load board.
Drip, Drip, Drip
Speaking of that capacity, there is a reduction happening, albeit a slow drip. As shown in Figure 1.2, for the past year and a half, almost two years, the biggest reduction in capacity has been from the owner-operator segment. Most likely, the carriers in this group that have exited the market are those that rushed in when freight and rates were plentiful, and now are finding more normalized rates combined with high overhead to be unsustainable.
As shippers continue to look ahead, not having reliability among this segment of carriers could prove problematic as volumes escalate and more freight flows to the spot market, which is supported heavily by owner-operator drivers. This is a good reason for shippers to ensure they have a good mix of carrier and broker partners.
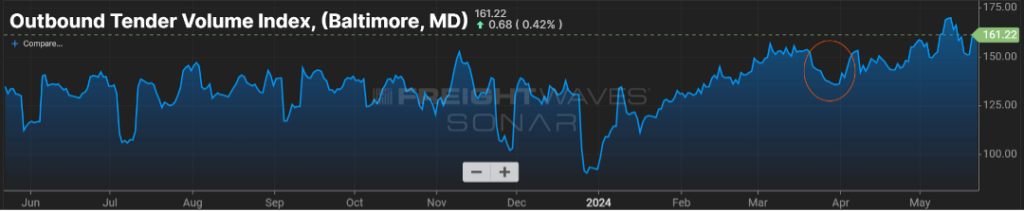
Baltimore Still Recovering
Finally, it has been just over three months since the bridge collapsed near Baltimore, MD. The waterways in the surrounding area appear to be returning to normal, and the need for traffic that populated the bridge to divert to alternate routes seems to be no worse for the wear on drivers.
Looking at volume in that market in Figure 1.3 since the end of March when the event occurred, after a slight dip when freight had to be re-routed, volumes as measured by the OTVI have increased just over 10 percent. Certainly, there is still work to be done, short- and long-term, but the Baltimore area appears to have powered through an unfortunate event.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
A LOOK AT THE PAST AND FUTURE OF THE FREIGHT MARKET
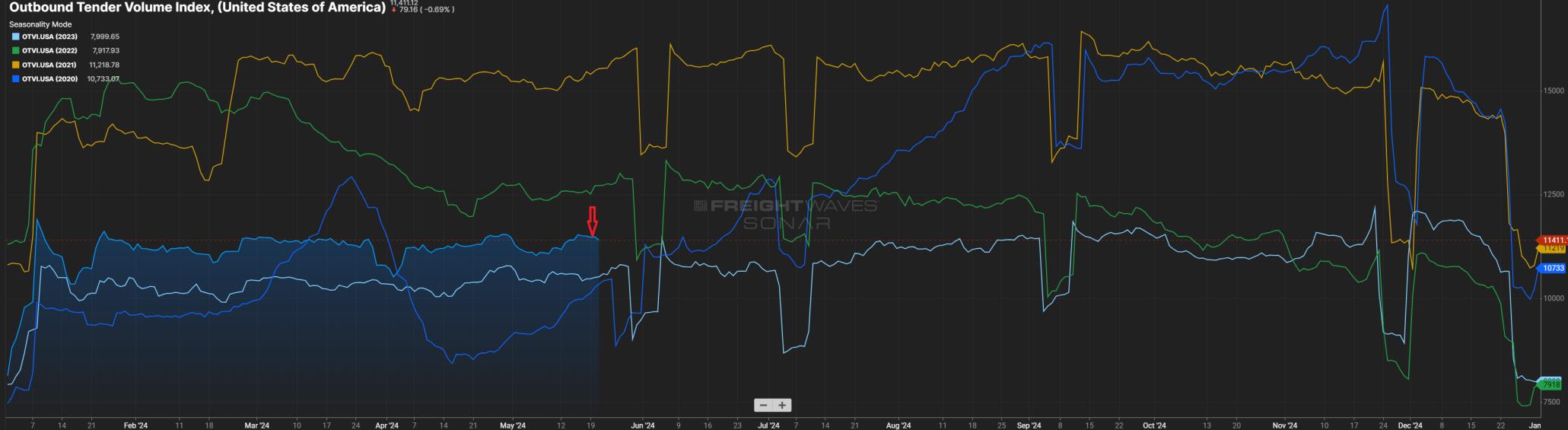
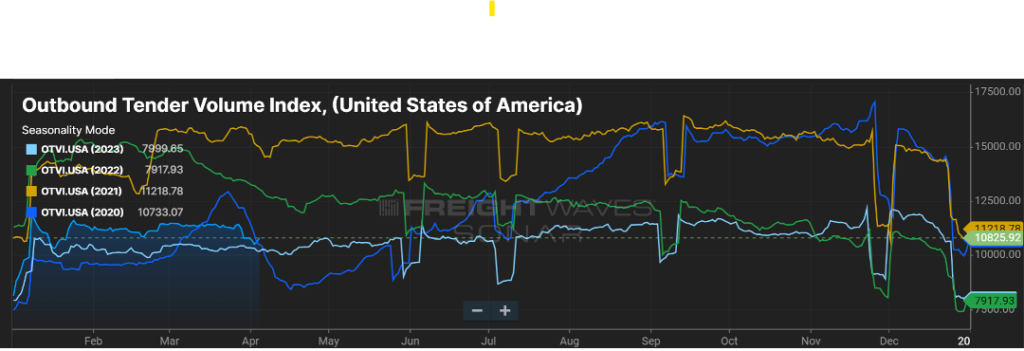
The Outbound Tender Volume Index (OTVI) measures the volume of contracted freight in the U.S. While this does not account for the spot market, ebbs and flows in contract freight have a direct impact on spot market volume and pricing. The outlier on the graph below (Figure 1.1) is the yellow line, representing calendar year 2021. This was an unprecedented year for freight volume, primarily influenced by consumer spending. While many feel the freight market is suppressed, that is not necessarily the case. 2024 will follow a more traditional freight flow pattern, with volumes up five to eight percent, year-over-year (YoY).
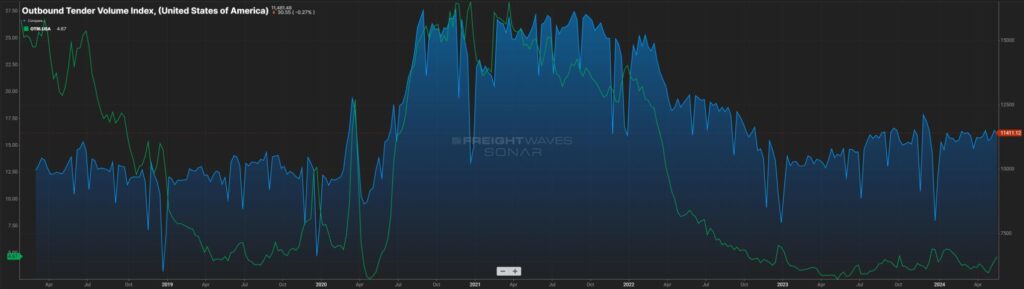
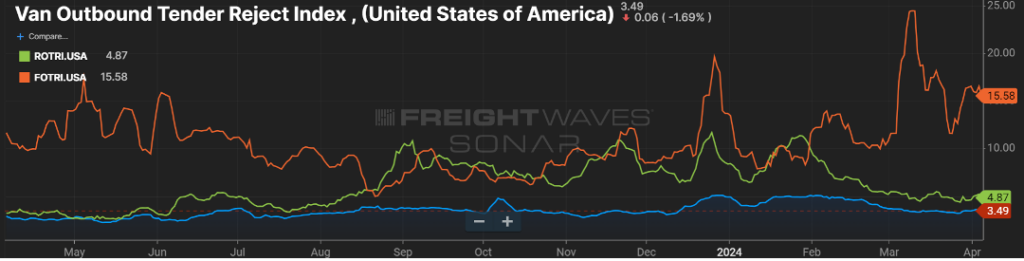
Measuring the freight volume is not enough to predict swings in pricing. Being able to overlay the frequency in which carriers say “no” to freight tenders via the Outbound Tender Rejection Index (OTRI) gives a good picture whether the capacity side of the market can handle those swings.
The below chart (Figure 2.1) looks at the amount of contracted freight volume (blue line) with the frequency of tender rejections (green line) overlayed. As can see, most of 2019 and the first part of 2020 saw a market where freight volumes were easily handled. This was a result of lower than anticipated freight volumes versus a glut of carriers in the market.
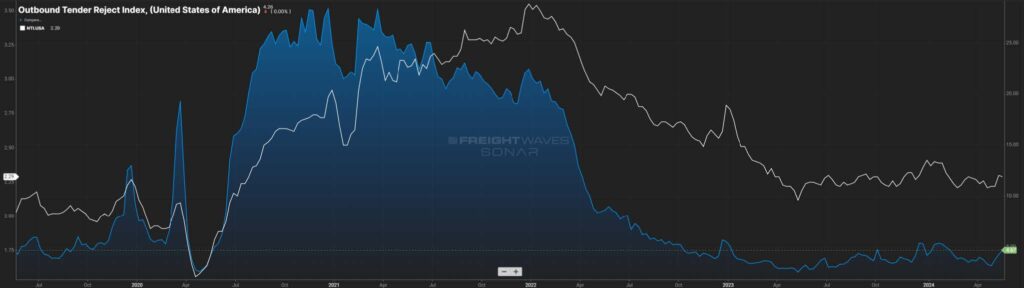
Then March 2020 happened. Everything went on lockdown. Volumes and rejection rates plummeted. That was quickly followed by a freight injection and for the latter part of 2020, and all of 2021, the market struggled with a lack of capacity to handle the record freight volumes.
For example, most LTL carriers were operating at 105-107 percent of capacity when they normally are in the low to mid-90s range. The freight market pendulum was in favor of the carriers. When the market gets hot, everyone wants in, which is what was happening in 2021, and 2022 – new carriers raced to get in on the action while existing carriers looked to soak up as much rolling stock as they could to capitalize on the market.
2023 saw a return to more traditional levels, but the capacity remained. As a result, rejection rates for freight tenders took a dive to below five percent, indicating carriers were eager for any freight that kept their fleets moving. This caused freight rates to take a dive (Figure 3.1) and then stabilize as of late.
But how long will shippers be able to rely on rate stability? Most likely the best determination will be the pace at which carriers exit the market.
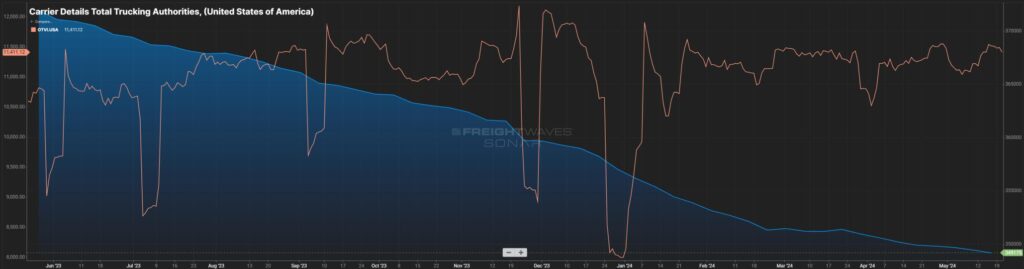
Figure 4.1 clearly shows capacity has been coming out of the market (blue line) for the past year. Most of that capacity is small – micro-fleets and owner operators. Certainly, this is dwindling capacity, but not to the extent of a large carrier pulling out of the market. A slow drip for sure.
The orange line represents the OTVI (volume) in the market, and that has slowly climbed over the last 12 months with the normal seasonal up and downs. At some point, as the volume inches up and capacity comes down, it’s simple supply and demand. Many are pointing to the end of this year, more likely spring of 2025 when that balance starts to shift. Now is the time for shippers to learn the contingency plans that are in place with their carrier and broker providers to account for this.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
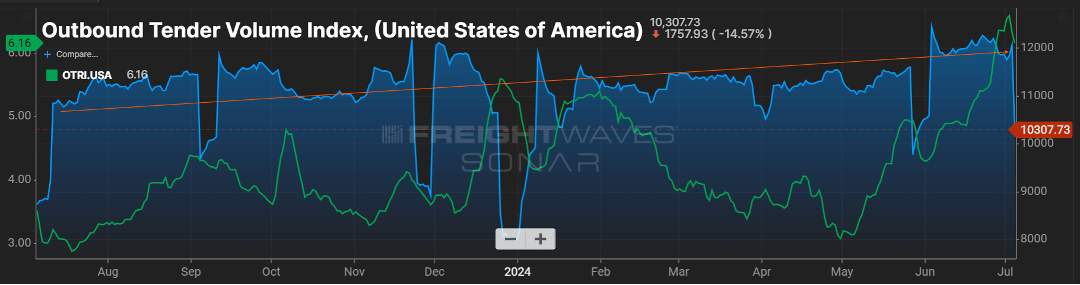
FREIGHT VOLUMES ARE ACTUALLY UP
It seems much of the news clippings have been around freight rates and how they remain suppressed. One could jump to the conclusion that this is a result of freight volumes being down. On the contrary, freight volumes are elevated from what we saw in 2023.
As you can see in Figure 1.1, volumes for the majority of 2024 are between six to eight percent higher compared to 2023. What is driving (or not driving) rates remains the capacity in the market.

Capacity is showing a net decline, albeit slower than expected. Much of that reduction is being felt in the less-than-10 tractor-fleets, so while the number of for-hire carriers is declining, the impact to actual trucks to haul freight is a slow drip.
That capacity continues to hold tender rejection rates at extremely low levels, meaning few loads are hitting the spot market. As a result, spot rates remain almost $0.70 per mile less than contracted rates. There has been some closing of the gap over the past year, as shown in Figure 1.2, but look for the gap to remain relatively consistent for the remainder of the year.

The Aftermath of The Francis Scott Key Bridge Collapse
It has been about six weeks since the bridge collapse in Baltimore. Removal efforts continue and certainly, a return to normal traffic flow is years away.
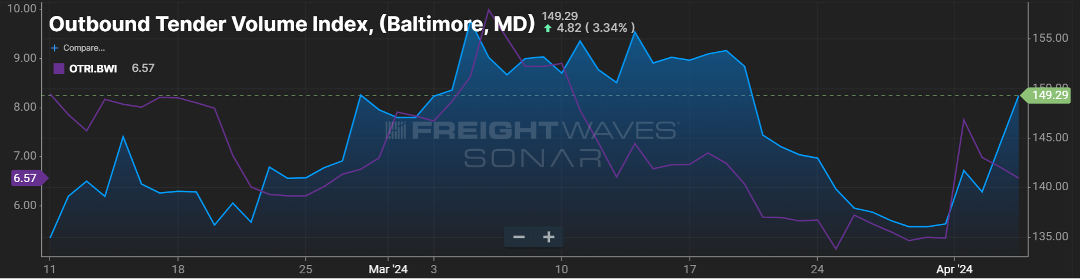
In positive news, looking at the *headhaul index for that market (Figure 1.3), aside from the drop around the time of the collapse, things appear to be back to normal from a balance standpoint. Certainly, there are more out-of-route miles and freight that may be entering at nearby ports, but for the most part, outbound and inbound freight volumes appear to be back to normal for the Baltimore market.
*headhaul measures the variance in outbound versus inbound freight

Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
FRANCIS SCOTT KEY BRIDGE IMPACT
Watching the video of the bridge collapse was surreal. To have that structure there one minute, then five seconds later be completely gone, was jaw-dropping. Certainly, our thoughts and prayers are with those whose lives were impacted by the collapse.
Since the incident, clean-up has begun and a temporary waterway has been established, but it will take a while for the port to fully recover, let alone the bridge itself to be rebuilt. While the 30,000 plus vehicles that regularly cross that bridge is a sizable number, it’s about one-sixth of the volume that uses nearby major thoroughfares like I-695 or I-95 in the Baltimore area. Still, that traffic will need to go somewhere.
From the trucking side, there will likely be two main areas of impact. First, local freight that is destined for ocean travel will now need to find another port of departure, likely destinations the ports of NJ/NY; Philadelphia; and Norfolk, VA. This means more freight will be heading out of the Baltimore area.
Figure 1.1 below shows that since the end of March, right around the time of the bridge collapse, outbound volume, and freight tender rejection rates, have trended upward. Second, freight that travels around the Baltimore area will likely incur more out of “normal” route miles if the bridge was part of its route.
More carrier miles = more time to deliver = less time for other freight = increased freight costs.
SOME BALANCE SEEN
Overall, freight volumes have trended slightly above 2023 (Figure 2.1).
This has not dramatically impacted freight rates nationally or freight tender rejection rates. Excess capacity continues its slow runoff, and March saw an uptick in for hire carriers.
On a more granular scale, flatbed freight seems to be more optimistic. As seasonal flatbed type freight, combined with an uptick in industrial production and manufacturing activity is occurring, it has pushed flatbed rejection rates to more normal levels over the past few months as seen in Figure 3.1.
Flatbed rejection rates reached their highest point in over a year recently, and a 15 percent rejection rate is indicative of a more balanced freight market, if only for a certain equipment type segment.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxStay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
WILL 2024 BE A FREIGHT REBOUND YEAR?
I certainly do not expect that we will return to freight volumes like we saw in 2021, and part of 2022. Now, I will never say never, but those were most likely once in a lifetime events. However, there are many signs that point to a potential for 2024 to see a rebound in freight volumes and carrier rates.
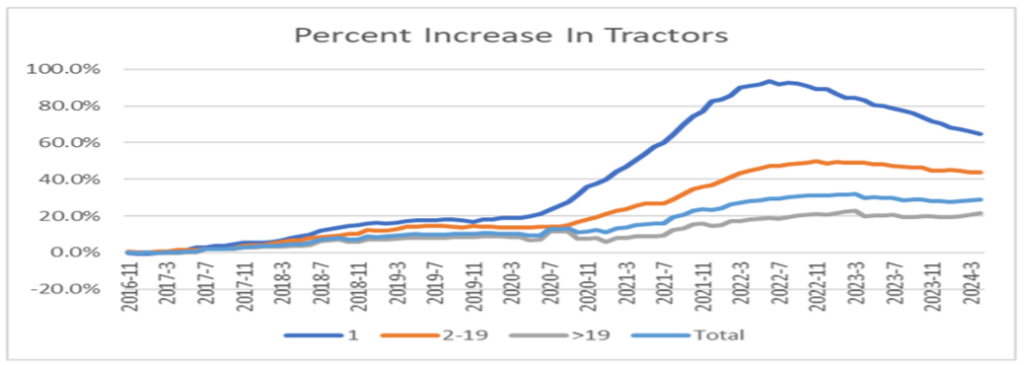
First, let’s talk about rates for over-the-road (OTR) carriers. Many new entrants came to the carrier market in ’21 and ’22, but currently, we’re seeing the contraction of for-hire carriers.
As shown in Figure 1.1, the past 14 months have seen less carriers in the market. As supply continues to dwindle, this will put upward pressure on rates. Granted, it may take another 12 months for the carrier market to find an economic balance.
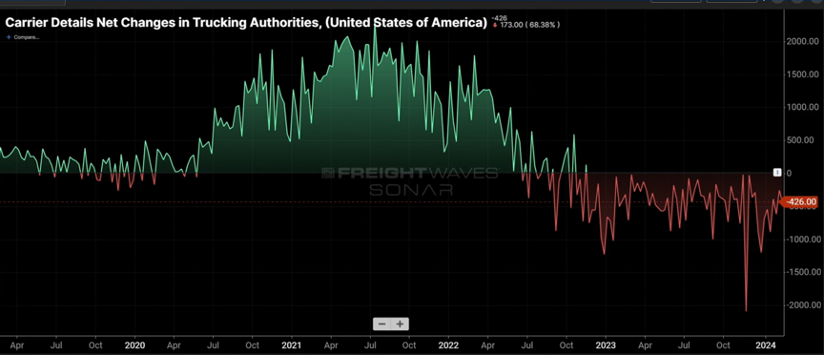
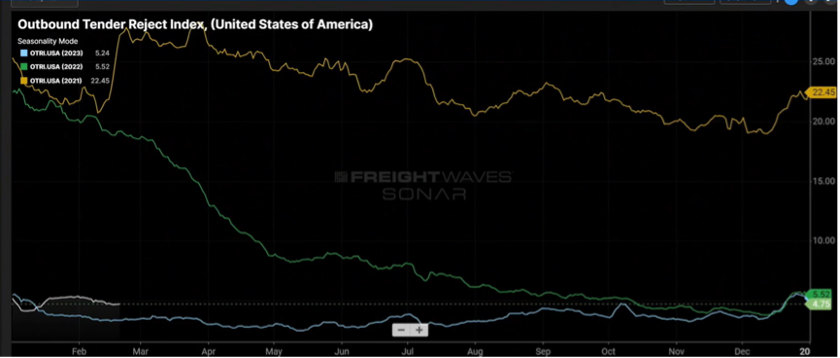
Figure 1.2 measures the rate at which carriers reject tenders (shipments) and continues to slowly climb upward. Granted, a rejection rate of five-plus percent is not earth-shattering, but in comparison to where it was in 2023, sub three percent in several months, five percent and the continuing upward movement is noticeable.
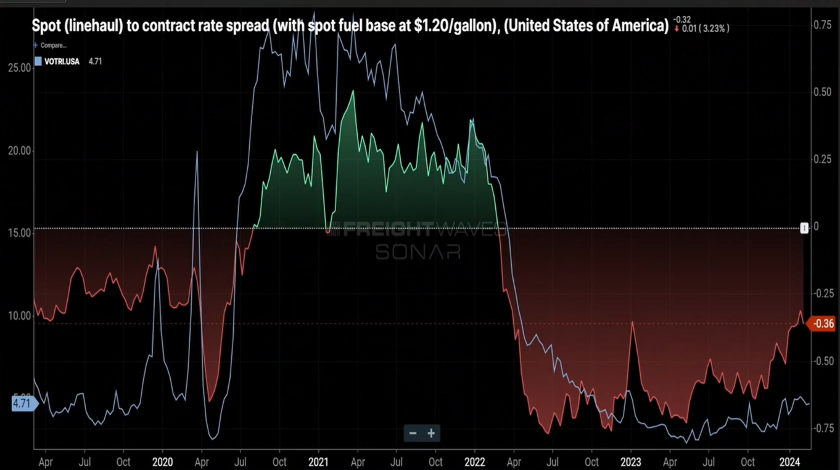
Lastly, Figure 1.3 shows that spot rates continue their slow rebound from the middle part of 2023. Contract rates throughout much of 2022 and half of 2023, were $0.60 to $0.70 cents per mile higher. Today, that gap stands at $0.36 per mile. This is a combination of spot rates inching higher, but also contract rates being less than prior years.
An Opportunistic Outlook
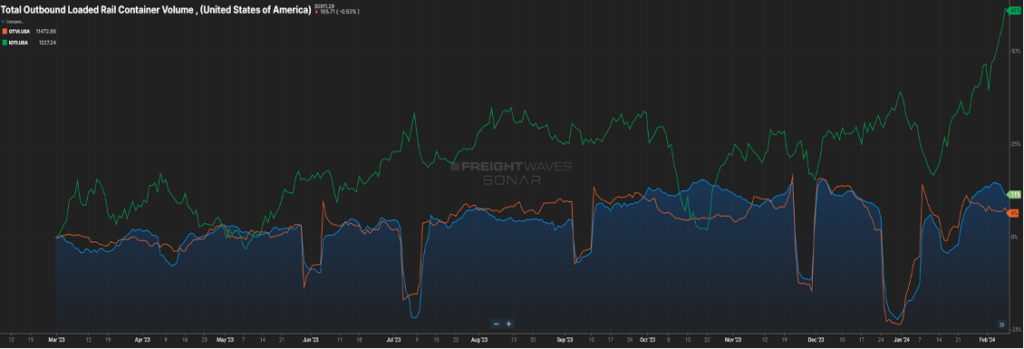
While contraction in the carrier market will influence the supply side of the economic equation, there also needs to be a demand component. The below chart (Figure 2.1) shows loaded rail car volume and over-the-road volume trending up and to the right, but the green line, representing inbound ocean containers, is really peaking.
Eventually, these containers will morph into rail and OTR volume. This is most likely a result in the drawing down of inventories, and the need for replenishment. Combine this with continuing increases in the manufacturing sector and housing market that will show better signs than 2023, it sets the stage for strong demand especially in the second half of 2024.
Will it be a bull or bear year in ’24? Well, if you would have asked that question six months ago, even maybe three months ago, my answer would have been slightly bearish or at best flat. However, seeing the recent signs on freight activity and the carriers needed to move this freight gives more reason to be optimistic as we go through the next ten months of the year.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your InboxAfter several record setting years, 2023 saw shifts to the freight market. How did the 2023 freight market affect shipper and carrier businesses? Did other businesses have the same struggles as yours? Are they expecting to face similar difficulties in 2024? How are their partner relationships?
Trinity Logistics wanted to get answers to these questions for you, so we asked a random sample of our shipper and carrier relationships to gauge the effect 2023 had on their business and what their expectations for 2024 in our first Freight Market Survey. Here’s what we found out:
2023 SHipper & Carrier Data: Freight Market Survey Results
Past Challenges – Same, But Different
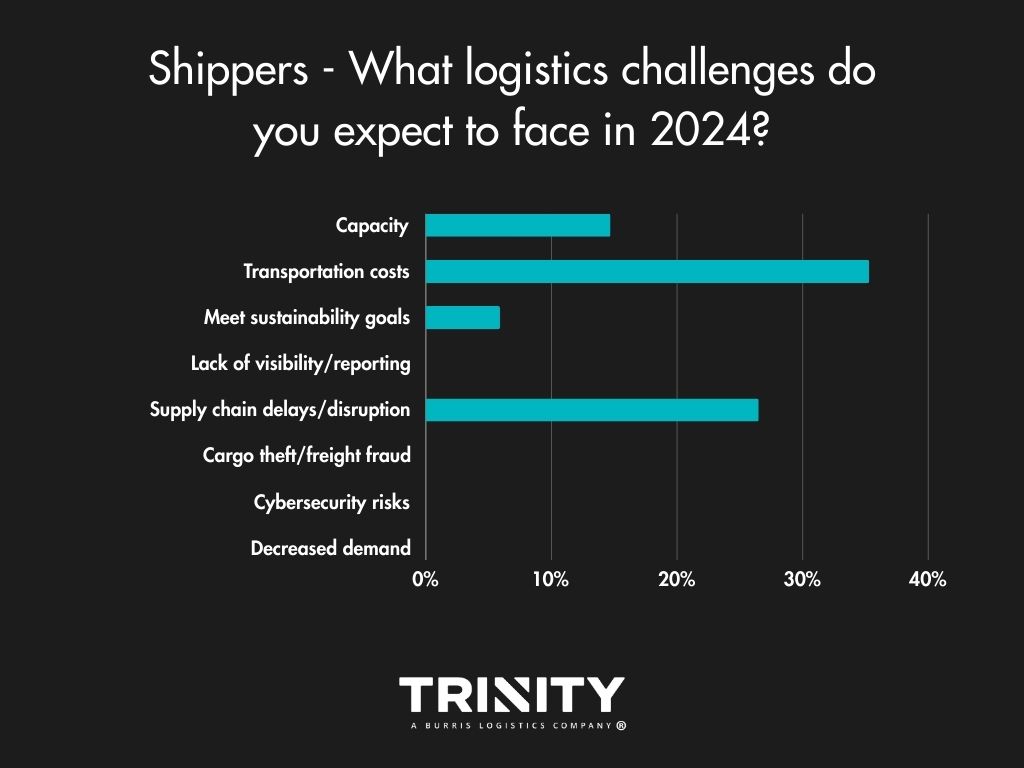
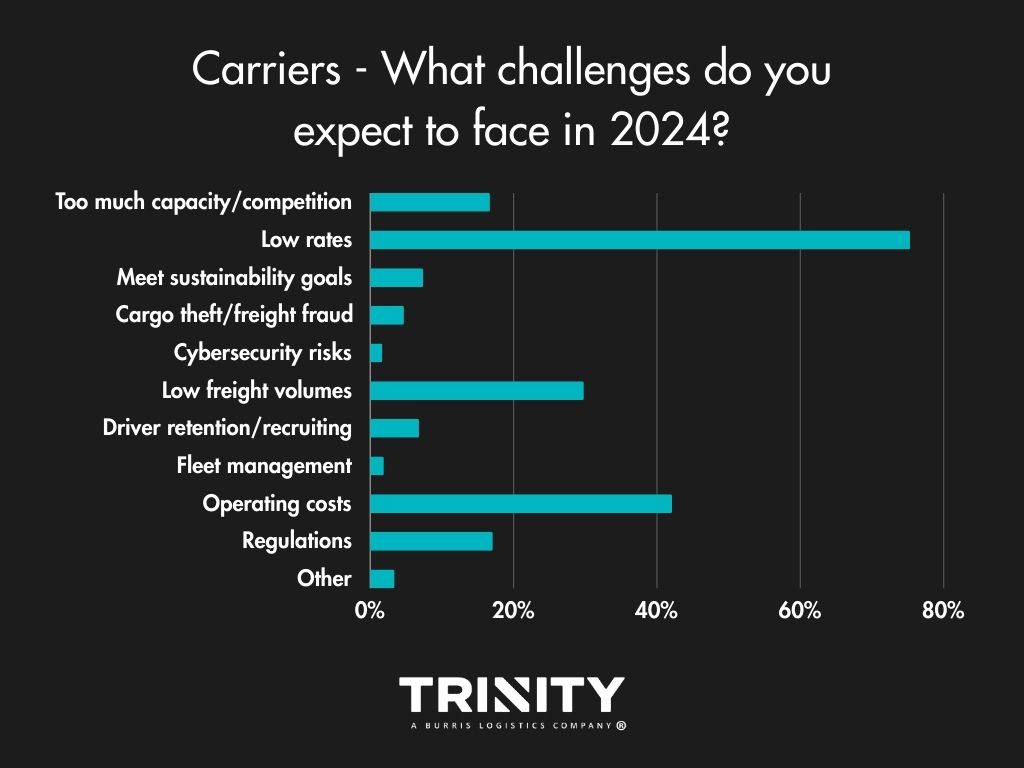
Considering the recent turndown of demand and the freight market, it’s not a big surprise that money was the biggest issue for shippers and carriers alike. Shippers answered that transportation costs were their biggest challenge in 2023, with supply chain delays/disruption and capacity not far behind. Low rates and increasing operating costs were the main challenges facing carriers.
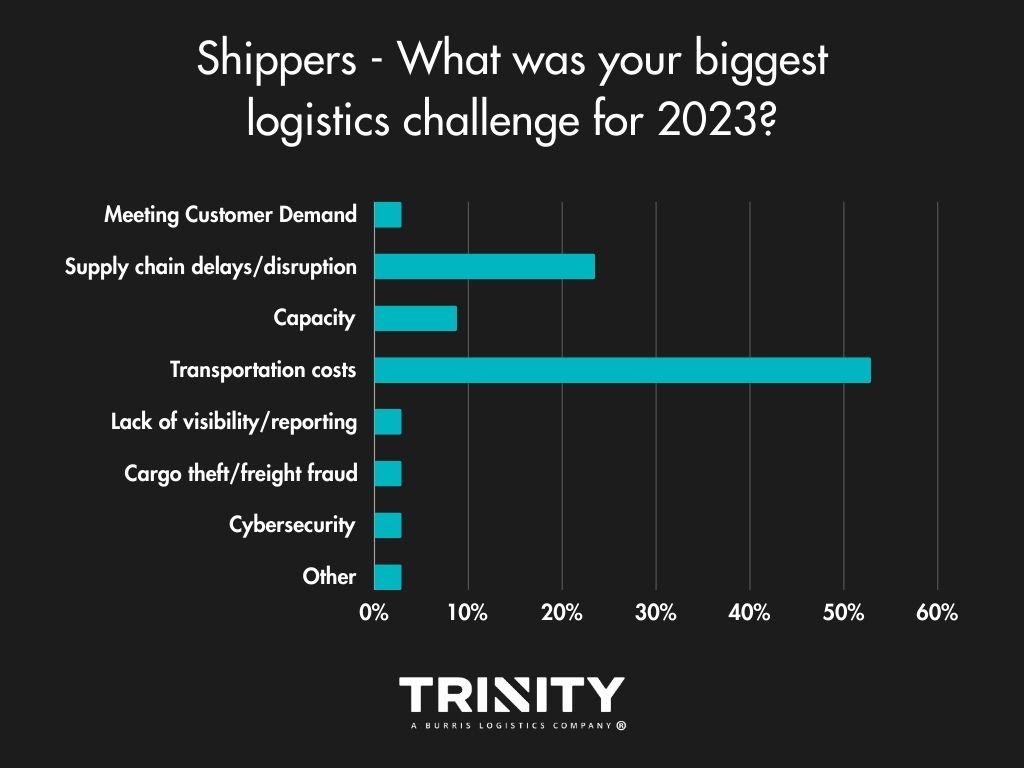
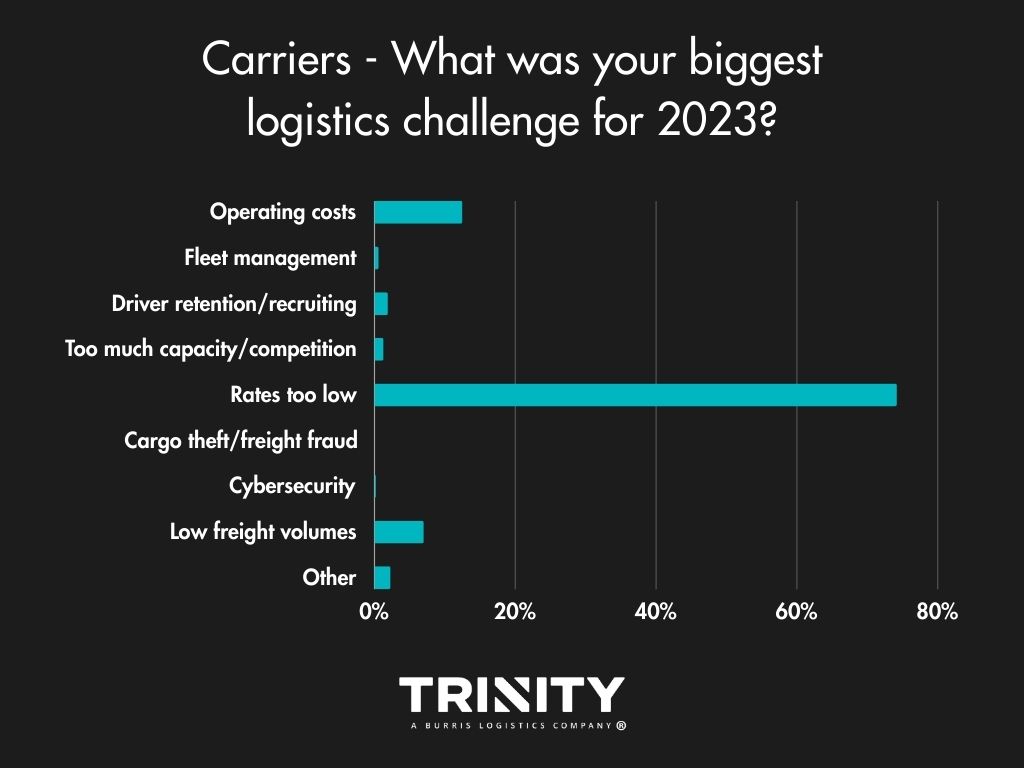
Business Impact – Could Have Been Better
Even with the change in consumer demand trending downwards throughout 2023, most shippers answered that their year was good overall. Carriers on the other hand seemed to face a rougher year in business with over half of them stating their year could have been better or was poor.
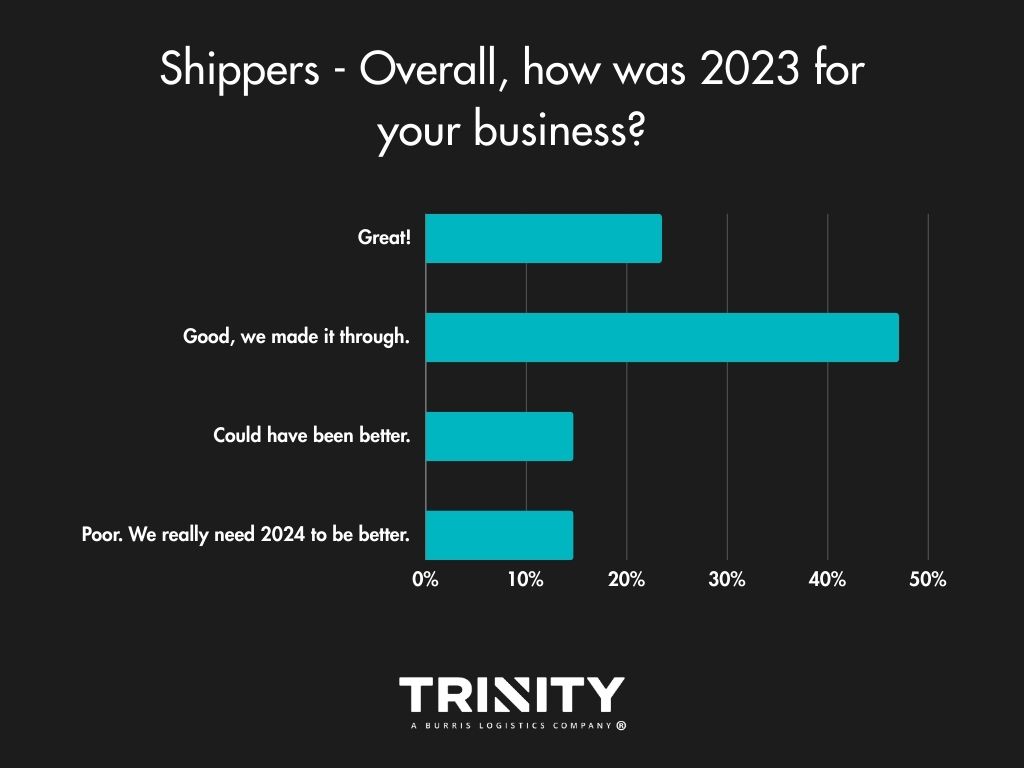
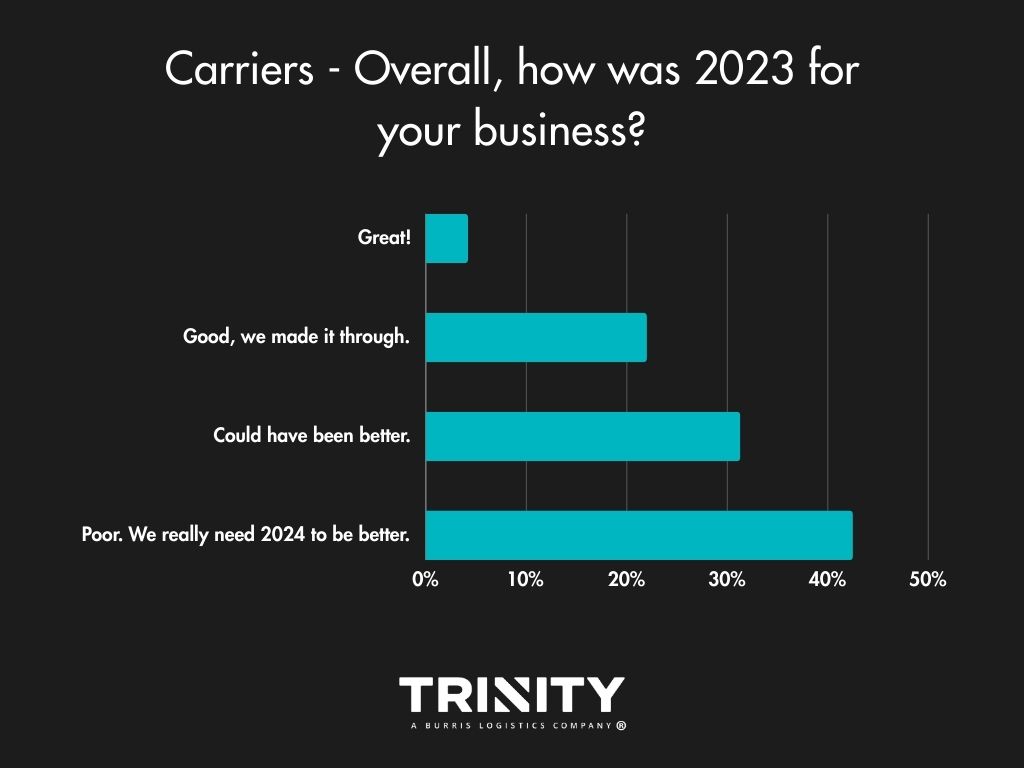
A LOOK INTO 2024
Future Challenges – Money Problems
2024 isn’t looking much different in terms of challenges compared to 2023. Shippers look to have the same financial challenges as they did in 2023 with transportation costs, supply chain delays/disruption, and decreased demand being the top concerns selected. Carriers are still concerned about low rates, operating costs, and low freight volumes hurting their businesses.
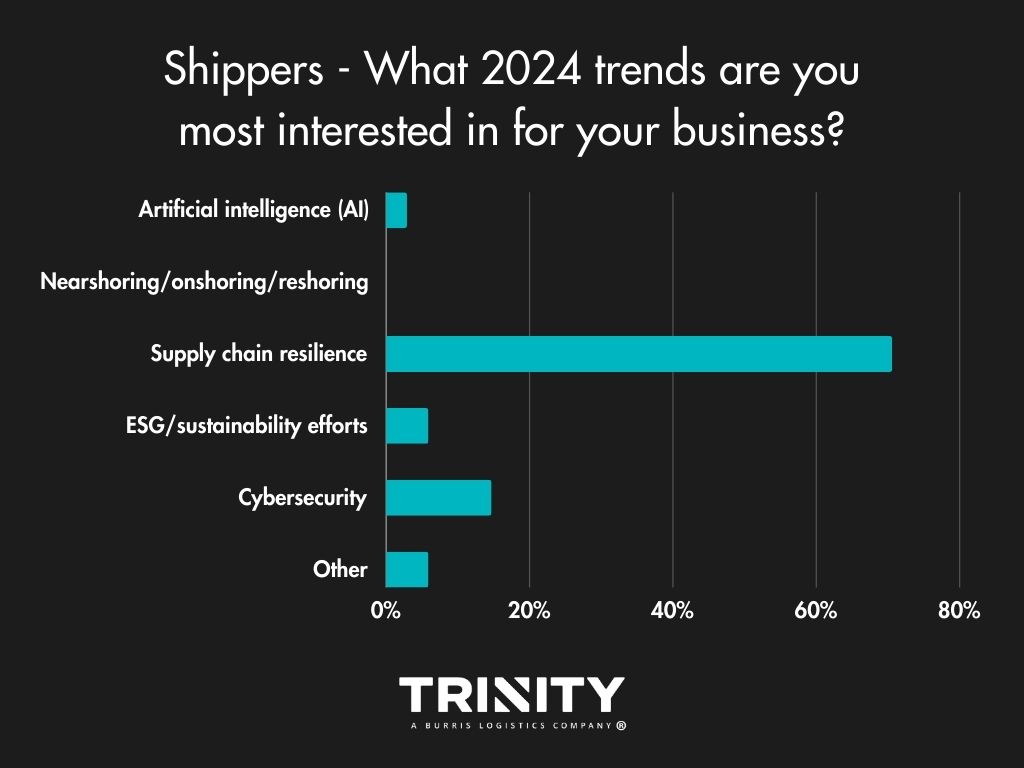
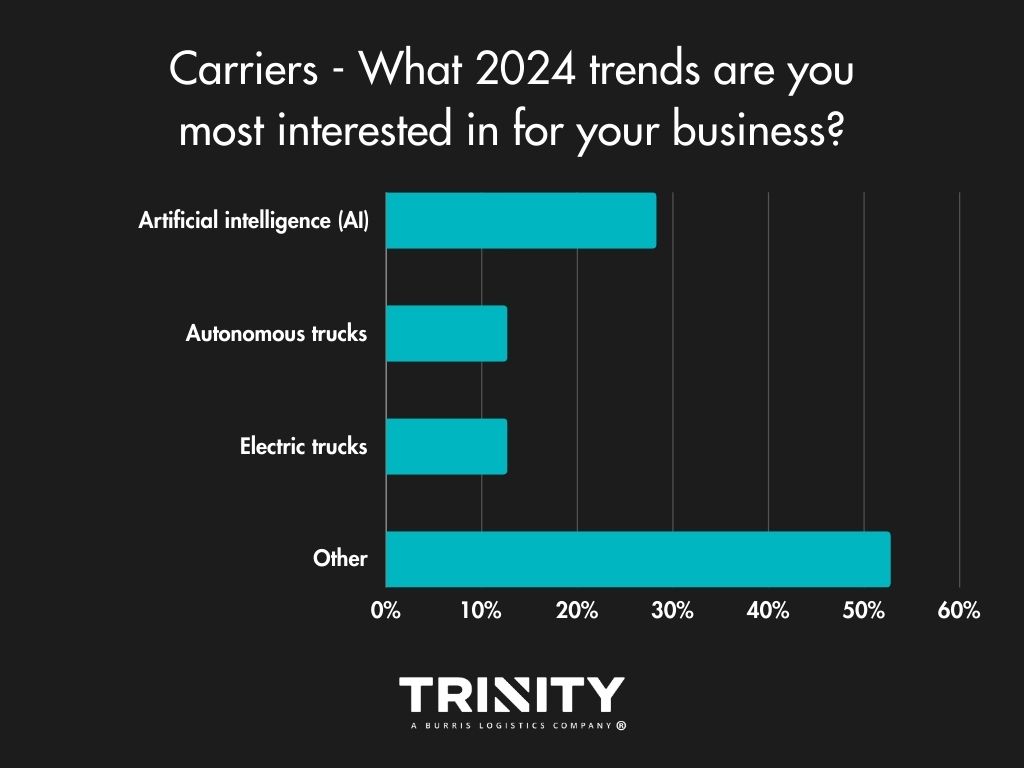
Hot Trends
Even though transportation costs are shippers’ strongest concerns in their previous answers, it seems the increased amount of supply chain disruptions and delays we’ve all experienced in these recent years have hit a nerve, with the majority answering that supply chain resilience is the trend their business is most interested in. Cybersecurity also looks to be a growing interest.
Carriers on the other hand, interestingly enough, look to the recent trend of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Also, as noted in the comment boxes of our “Other” option, increased rates and better fuel prices were trends they’d like to see in 2024.
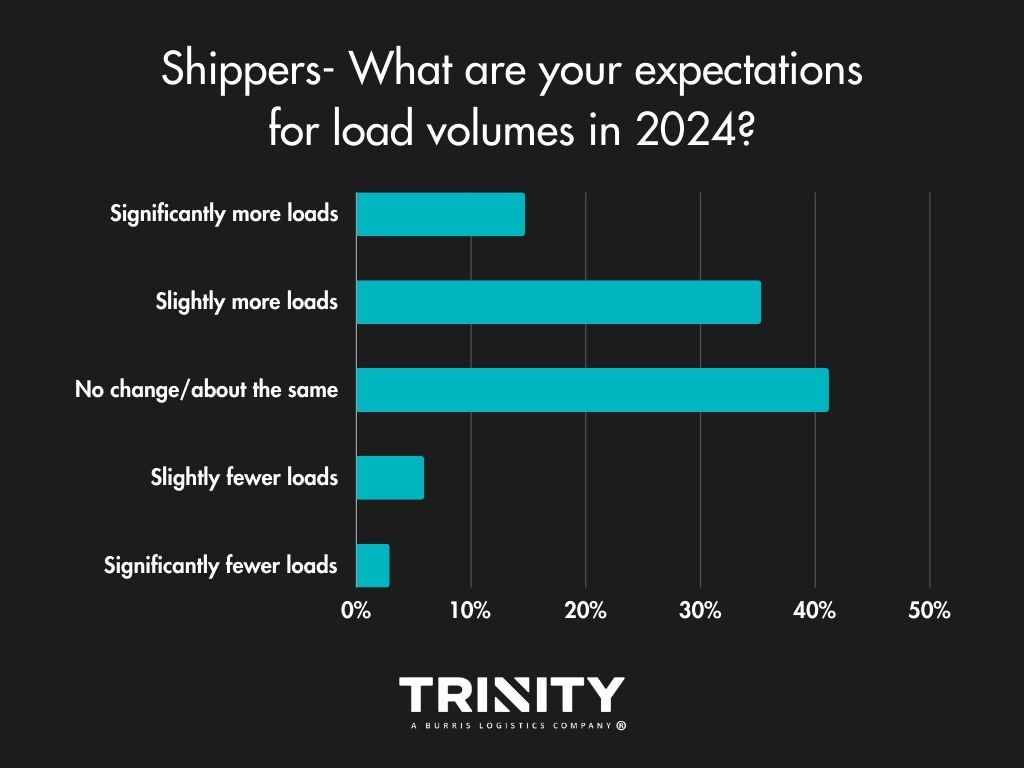
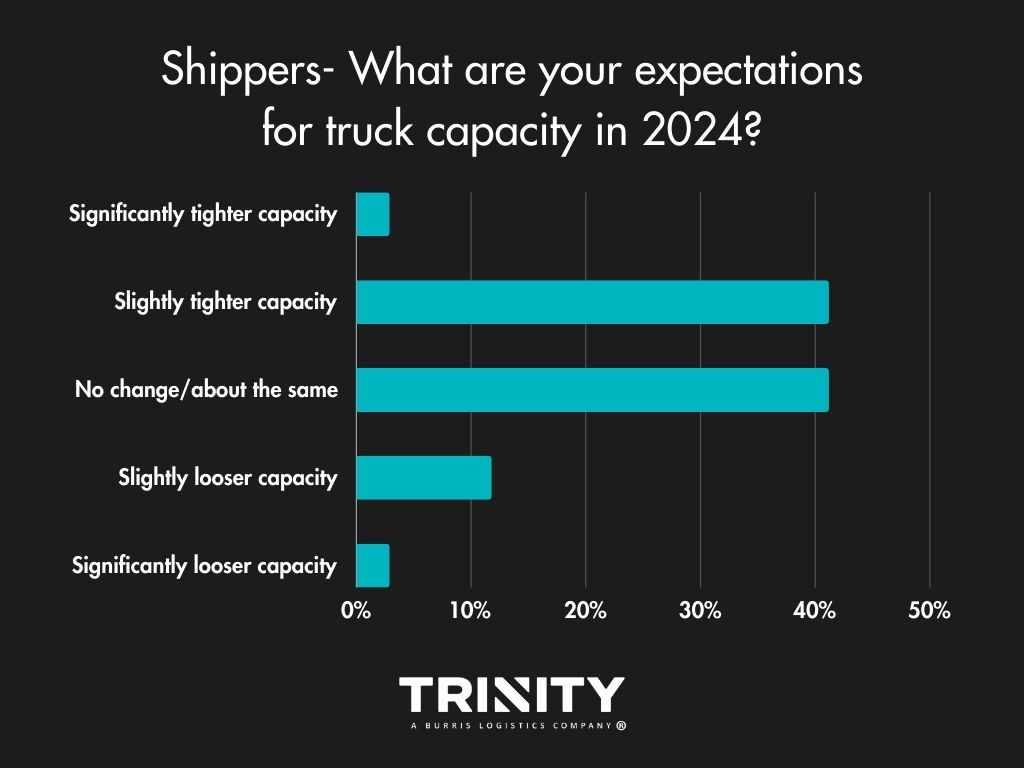
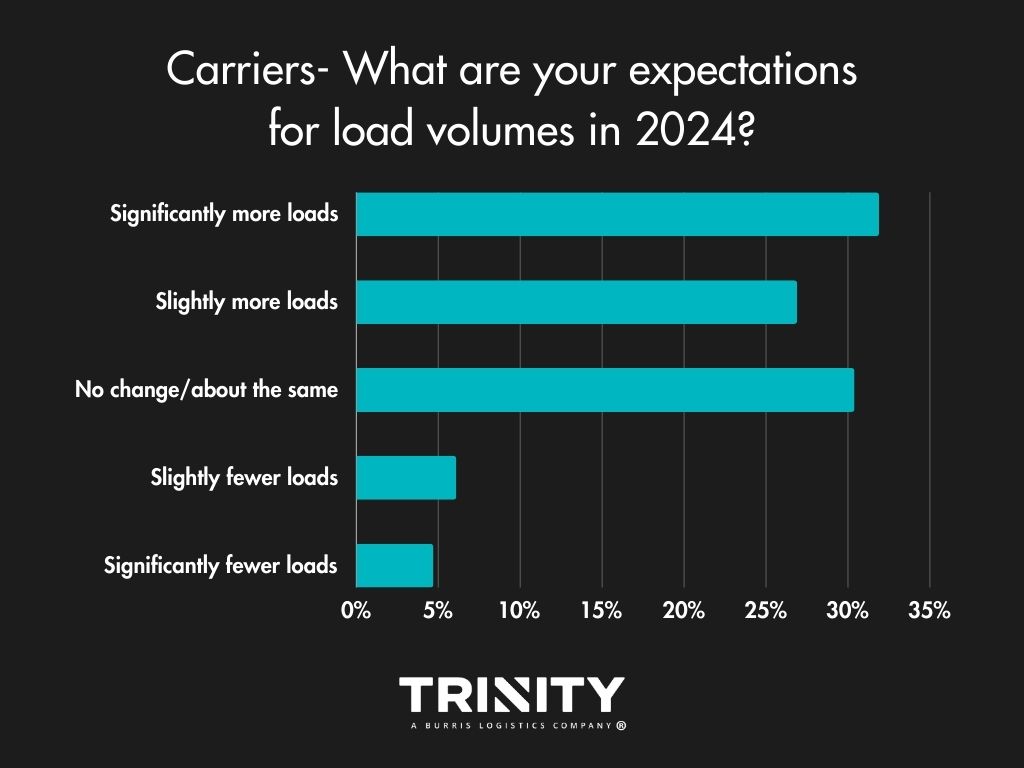
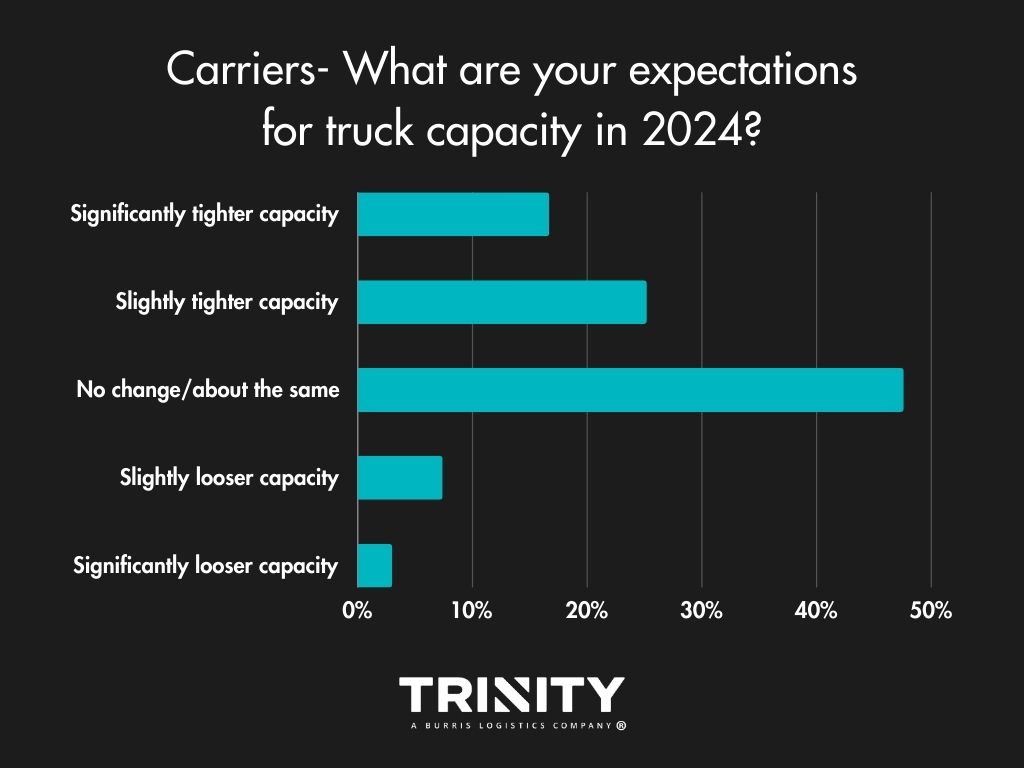
Load Volumes & Capacity – Slightly Positive Outlook
Overall, shippers are slightly more optimistic for 2024, thinking it won’t bring any change or the change it brings will be positive. Most think load volumes will stay the same or there will be a little more in freight volumes this year. As for truck capacity, they think it will be the same as 2023 or slightly tighter.
Carriers also think 2024 will bring more freight volumes and that capacity will likely stay the same or get tighten slightly versus 2023.
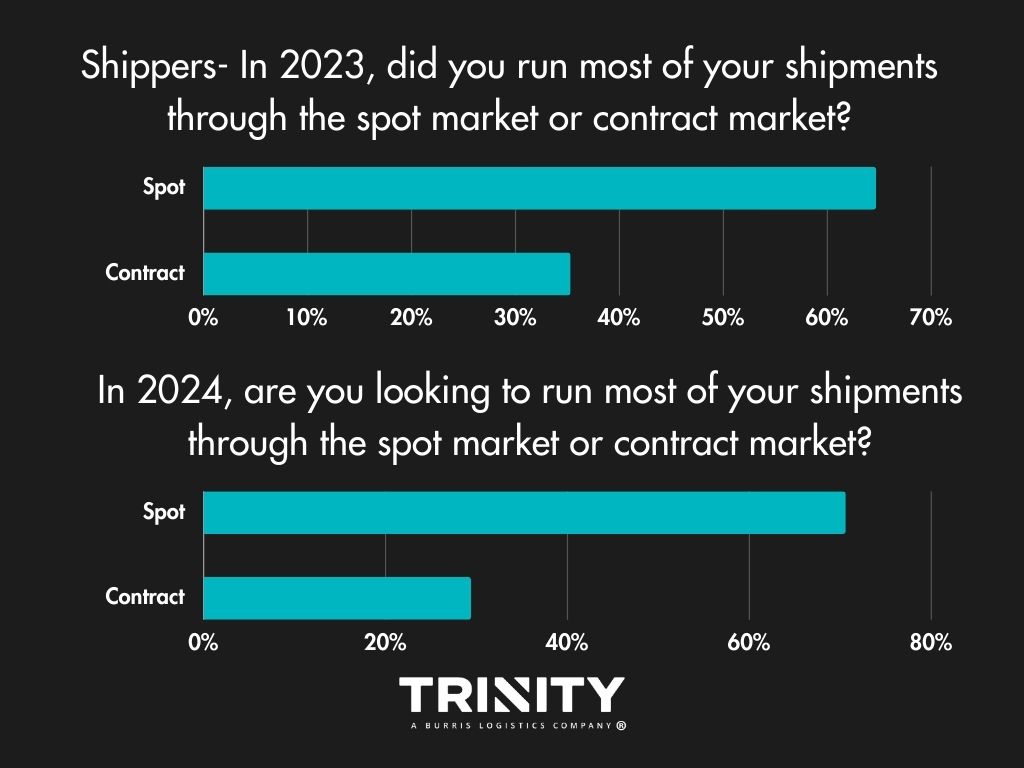
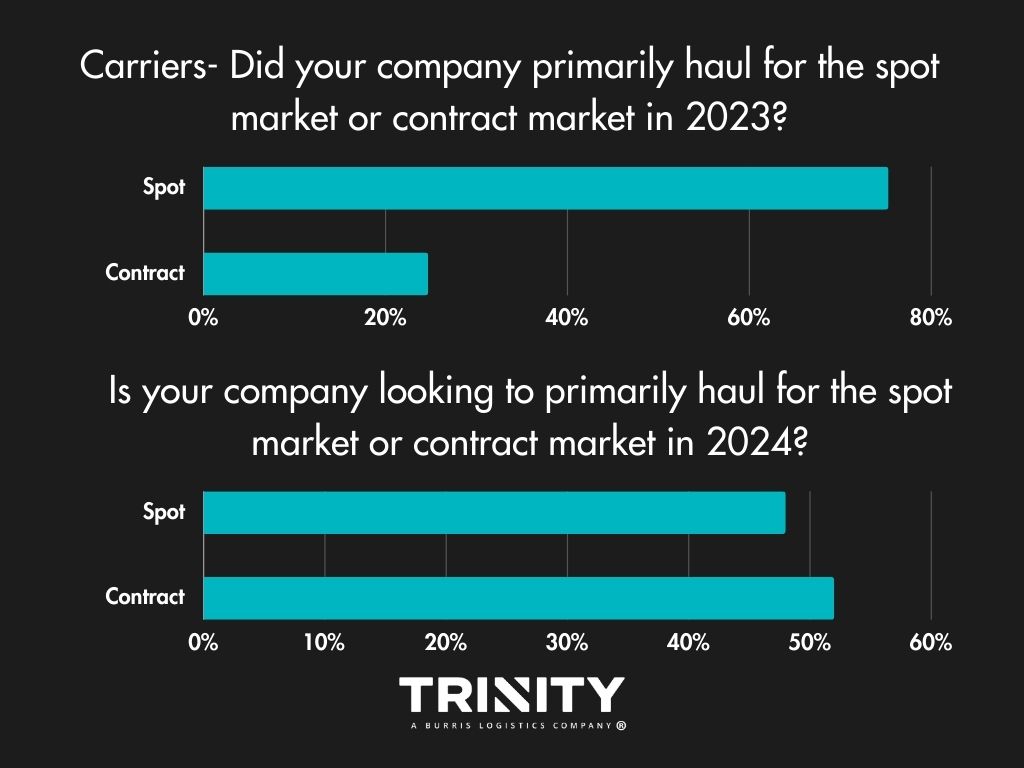
Spot or Contract?
Year-over-year, shippers aren’t looking to change much in terms of which market they turn to. Most look to continue to put most of their freight on the spot market.
For carriers, there looks to be some change anticipated. In 2023, most carriers ran spot market freight but in 2024, over half of them look to haul contracted freight.
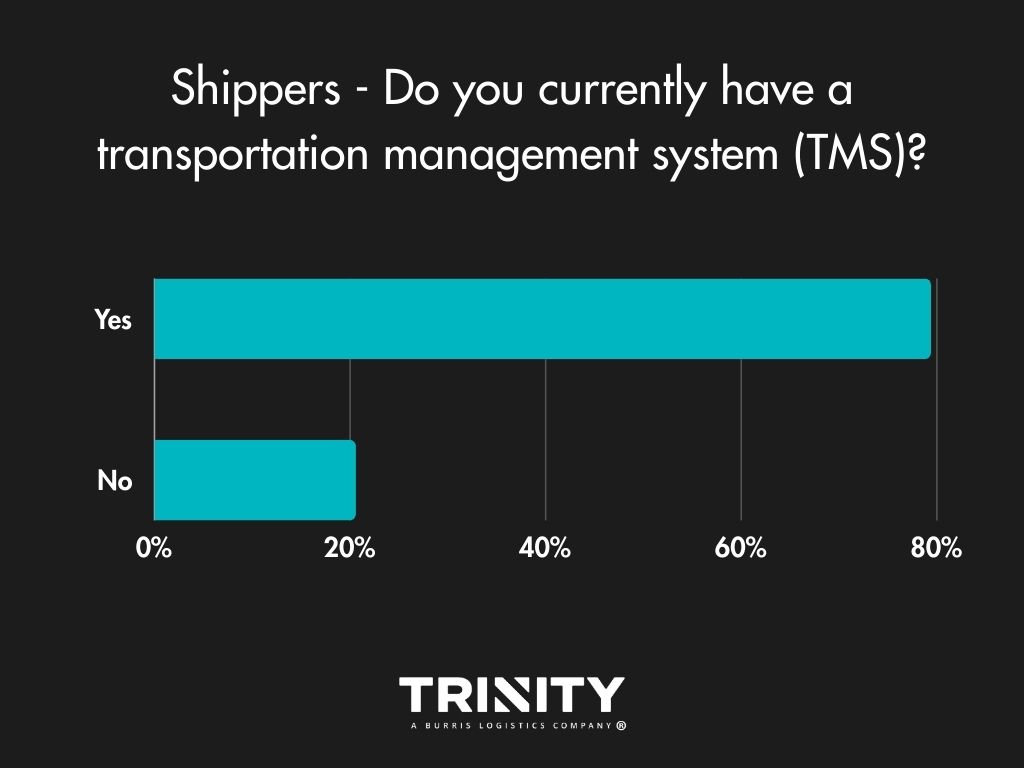
Do Shippers Have a TMS?
It’s 2024, so you’d think most shippers would have a transportation management system (TMS), and no surprise, they do. For those that don’t and answered, it seems they did not have a good experience with one in the past or don’t know enough about them.
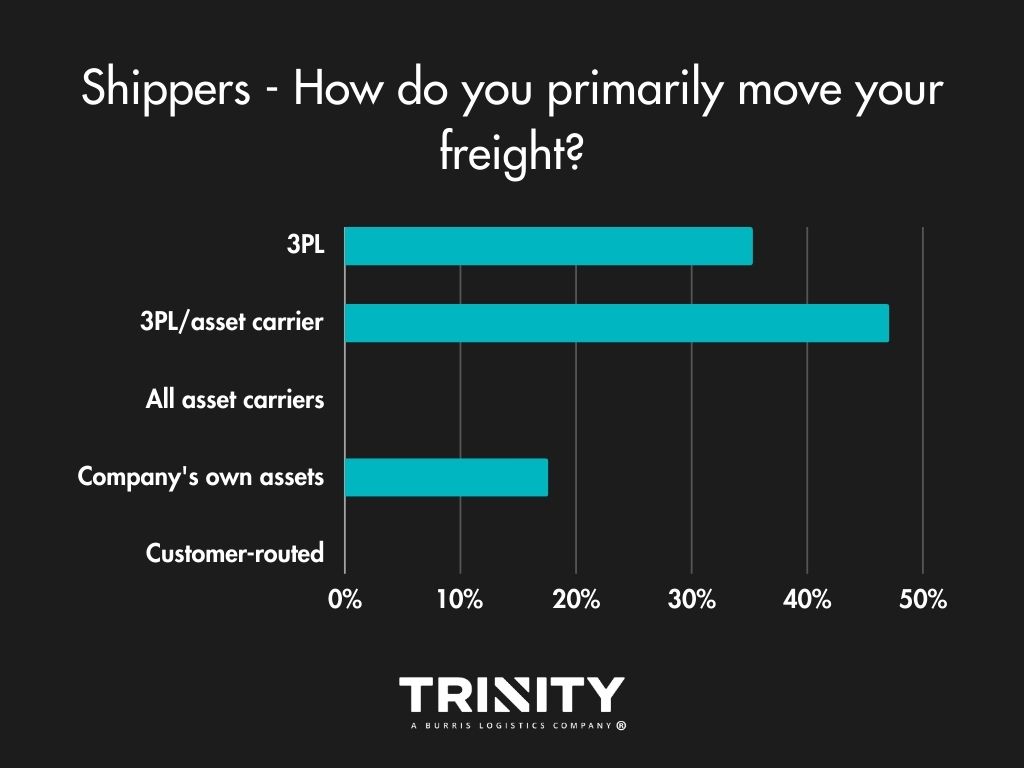
Brokers Are the Way to Go
When asked how they like to move their shipments, most shippers use a mix of carriers and third-party logistics providers (3PLs) or just 3PLs. A few do use their own trucks. For those that do outsource to 3PLs, they usually just stick to one provider.
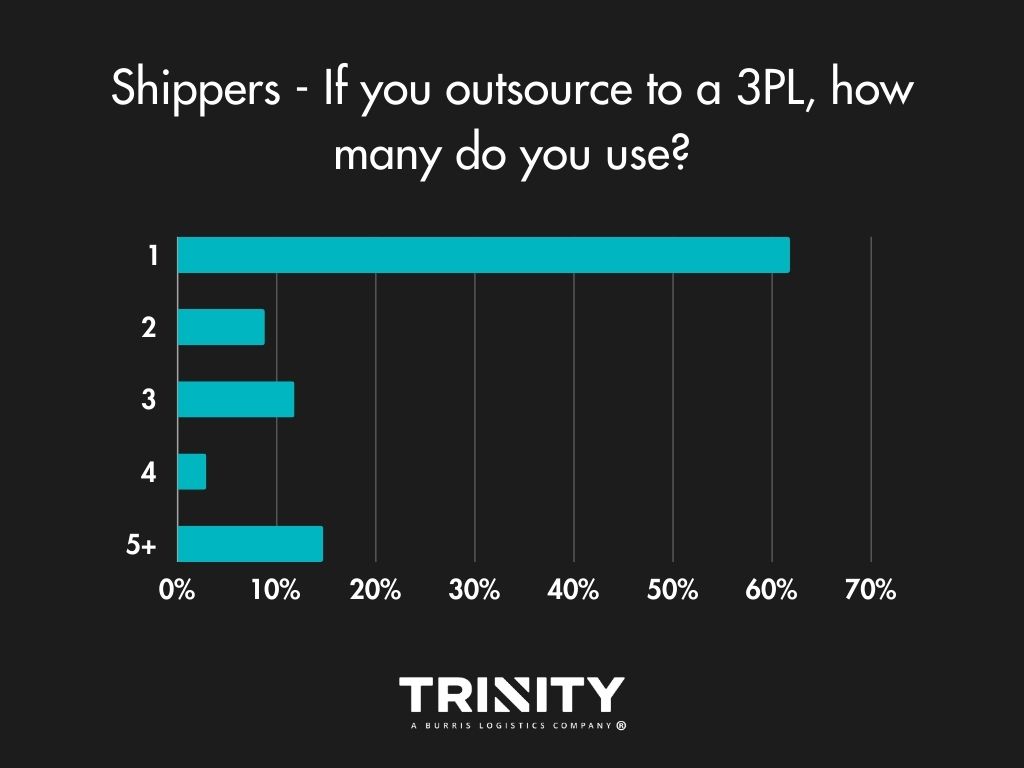
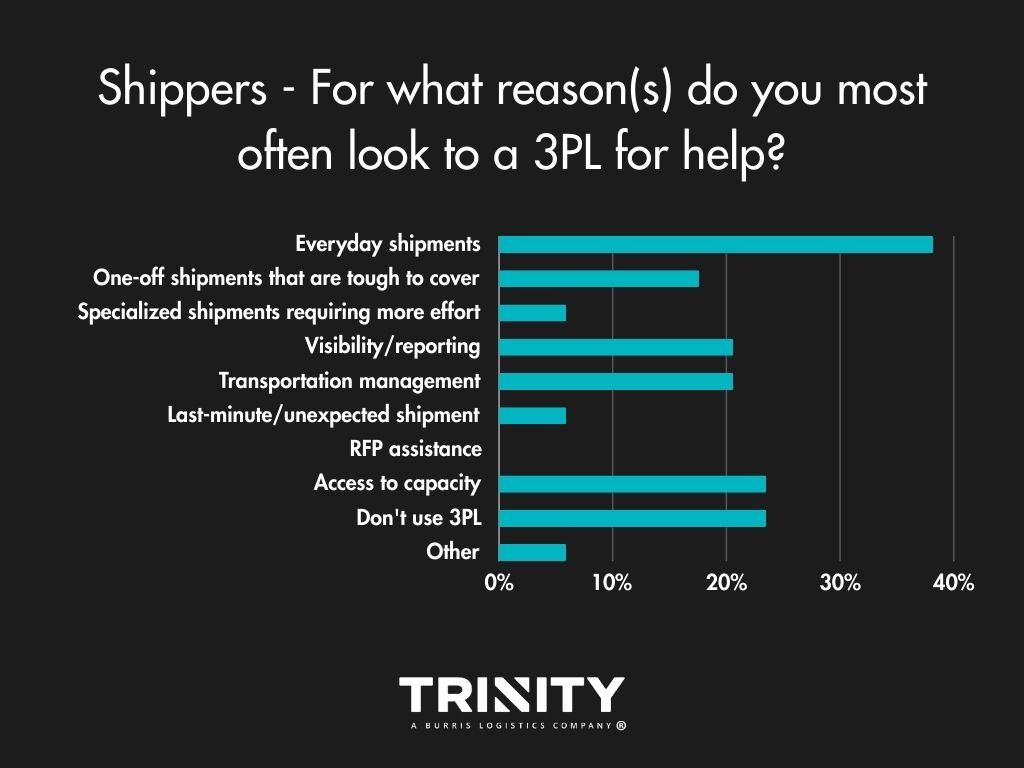
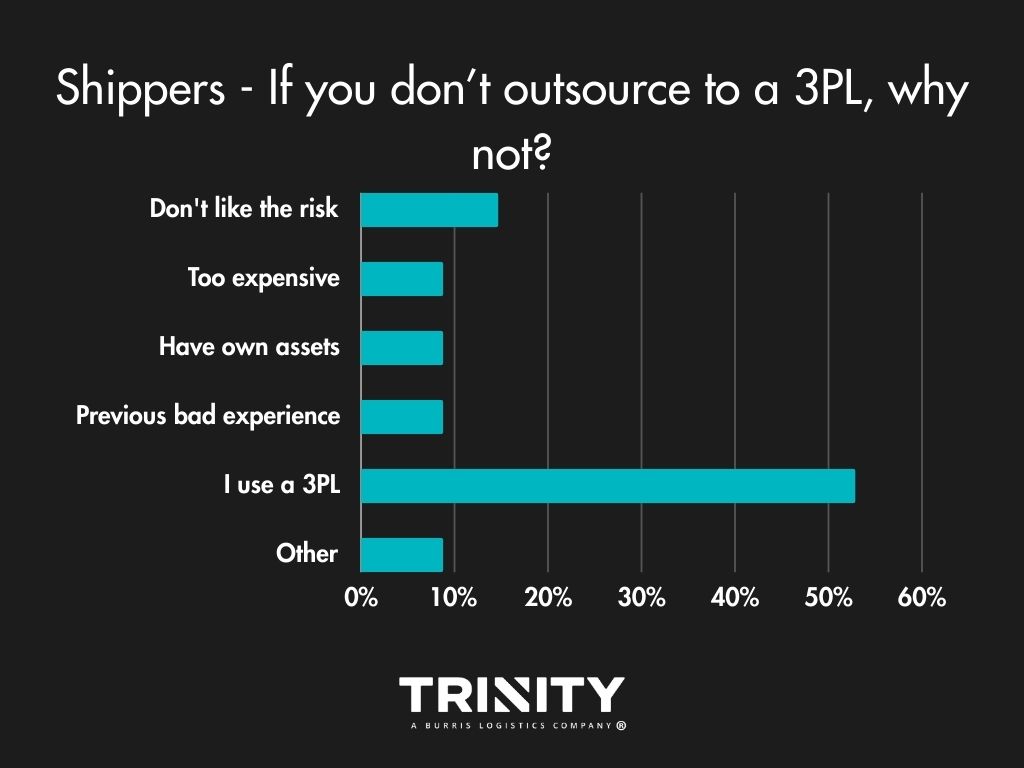
Shippers most often look to a 3PL for help with their everyday shipments, for transportation management, visibility, and access to their capacity. The main reason shippers choose not to work a 3PL for their logistics? They don’t like the risk.
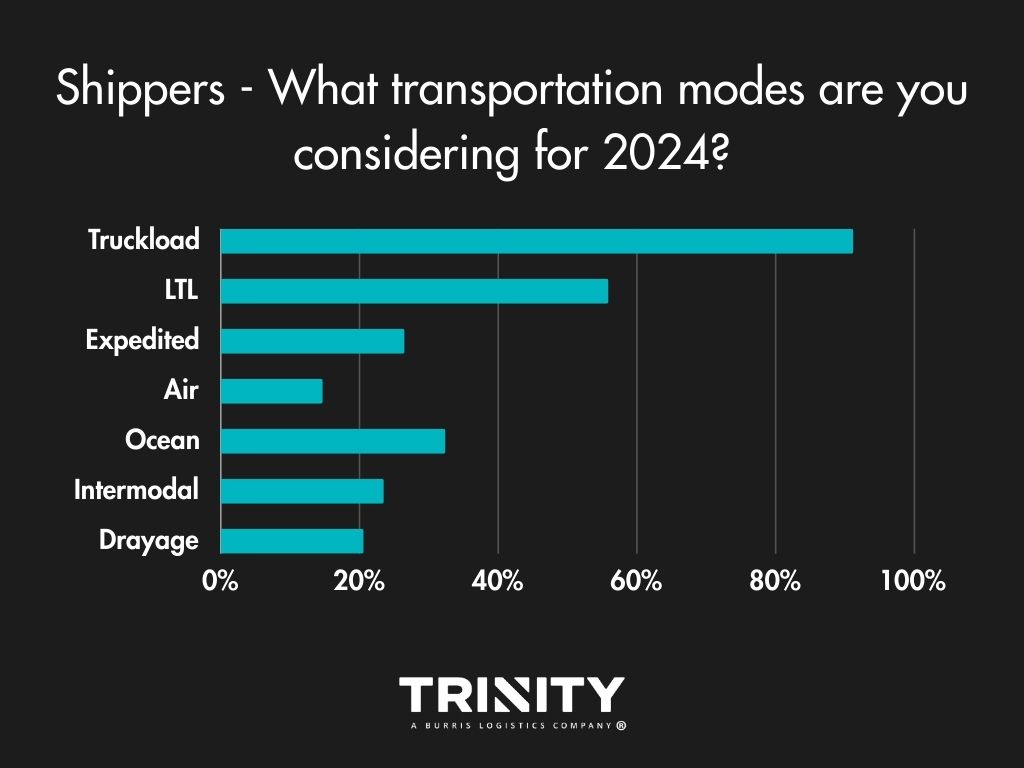
Transportation Modes – Staying Consistent
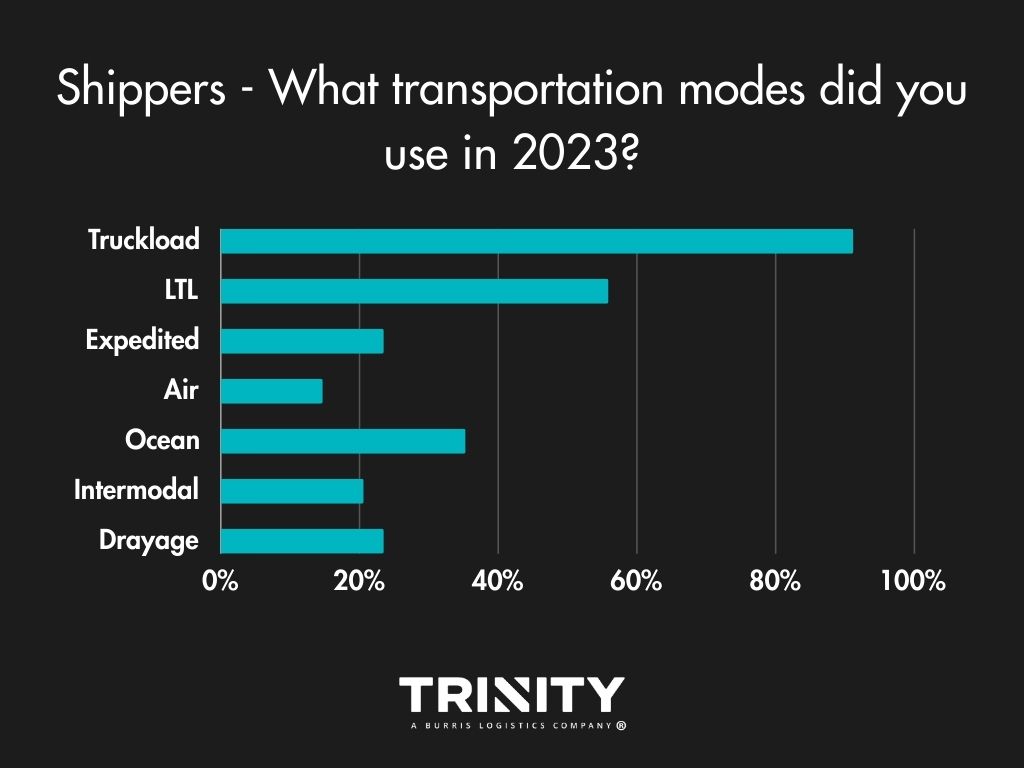
Overall, shippers aren’t looking to change what transportation modes they use for their shipments. Truckload and less-than-truckload (LTL) are the primary modes they like to use, with a little diversification sprinkled in.
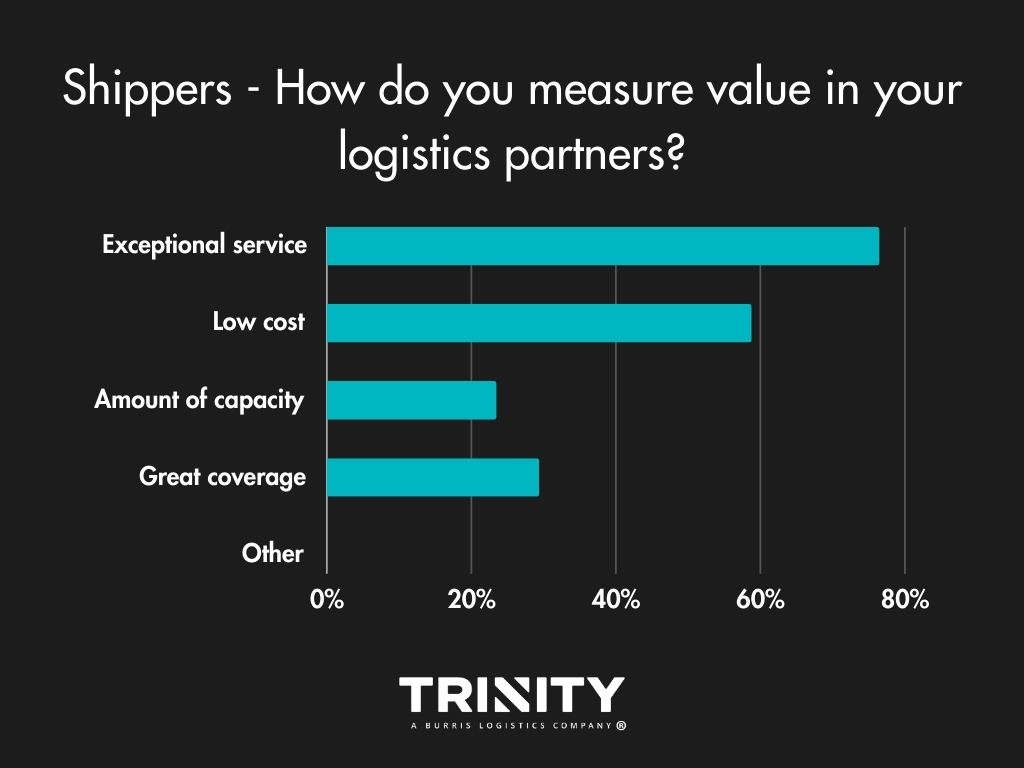
Exceptional Service Stands the Test of Time
When it comes to their logistics partners, shippers find the most value in receiving exceptional service, with costs coming in as a close second.
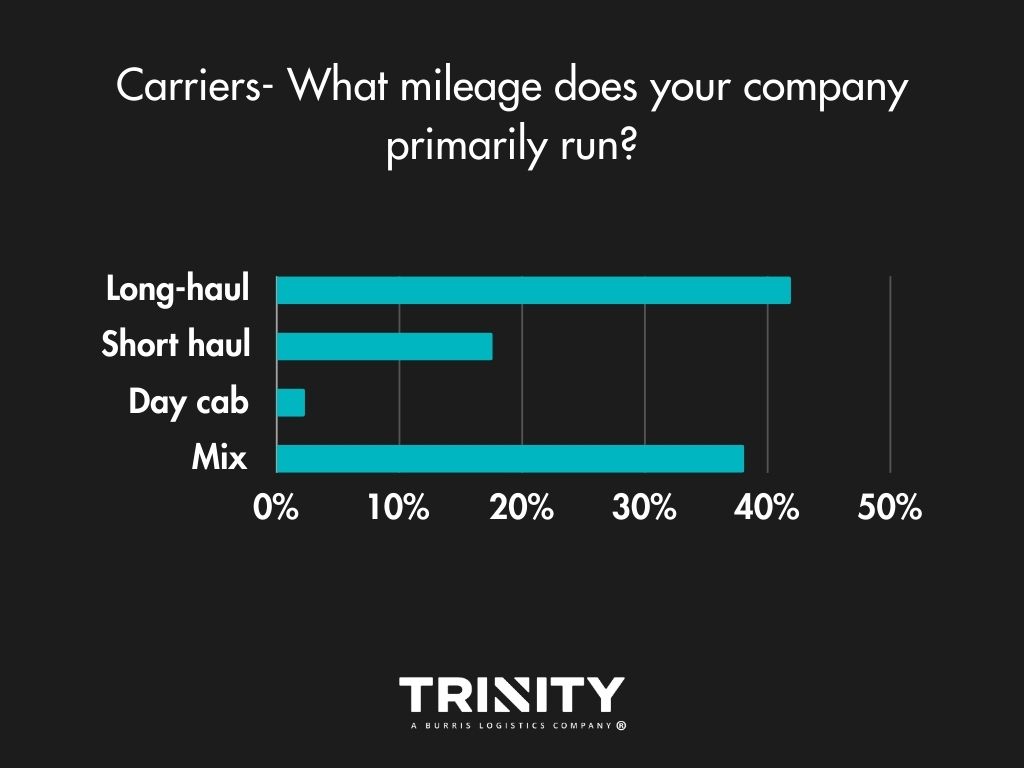
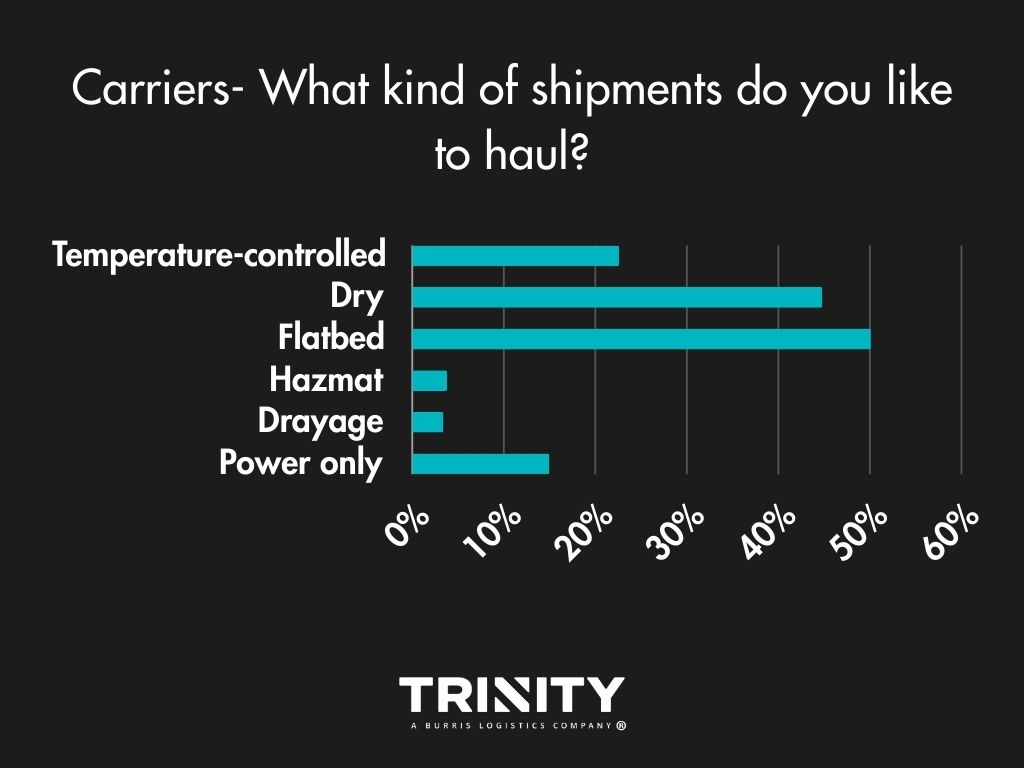
Most Wanted: Long Mileage, Flatbed Shipments
When it comes to mileage, most carrier companies tend to run long-hauls or a mix of short and long shipments. Flatbed hauls are the type of shipments most carriers like to haul with dry van coming in as a close second.
Load Boards are the Way
With 74 percent selecting this option, load boards are the norm for carriers to find available shipments. Sometimes they use their shipper relationships, and occasionally they make use of a 3PL.
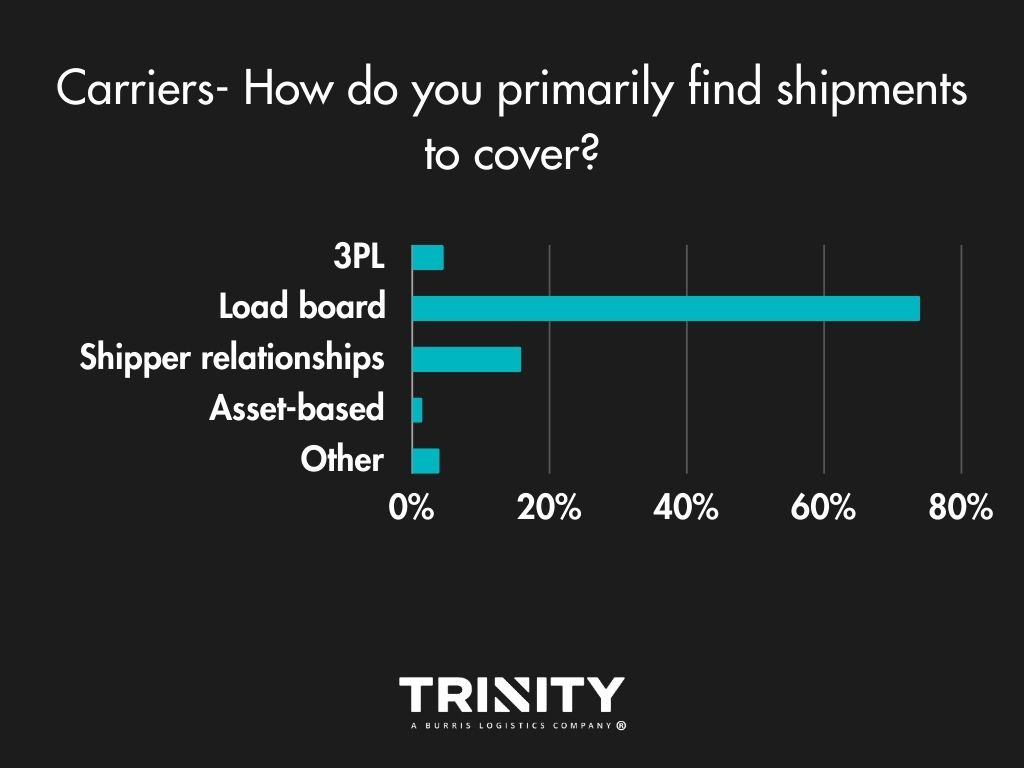
3PLs – Expanding a Carrier’s Reach
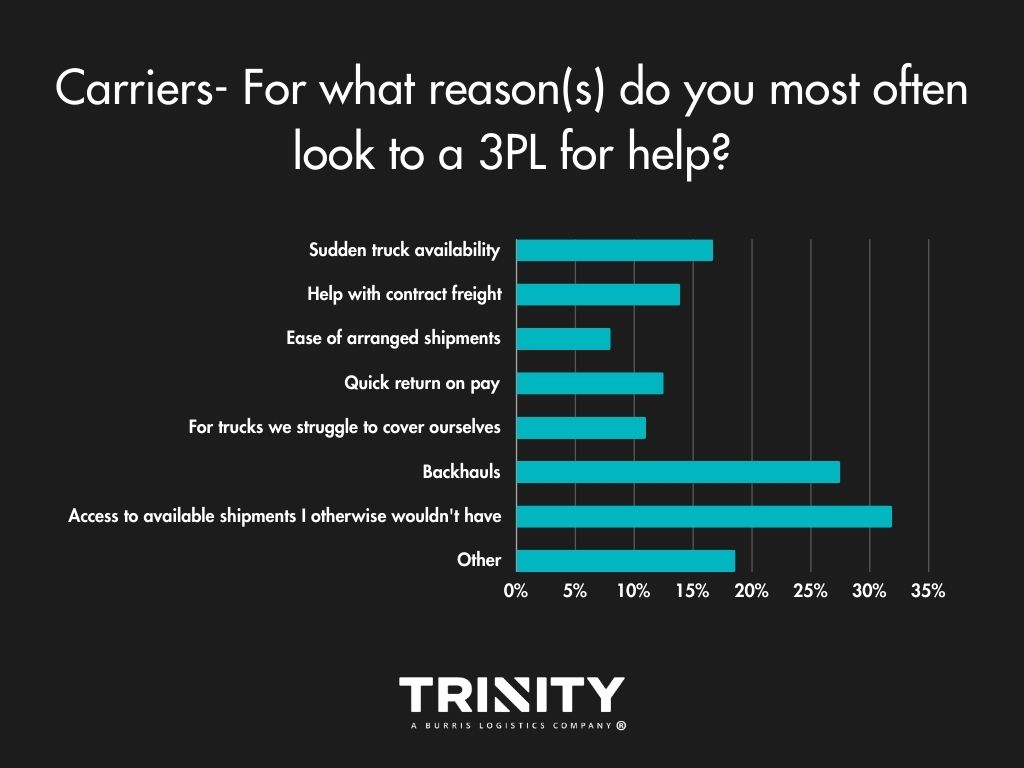
Carriers most often look to a 3PL for help with gaining access to available shipments that they wouldn’t have otherwise. Covering backhauls are another big reason carriers reach out to a 3PL.
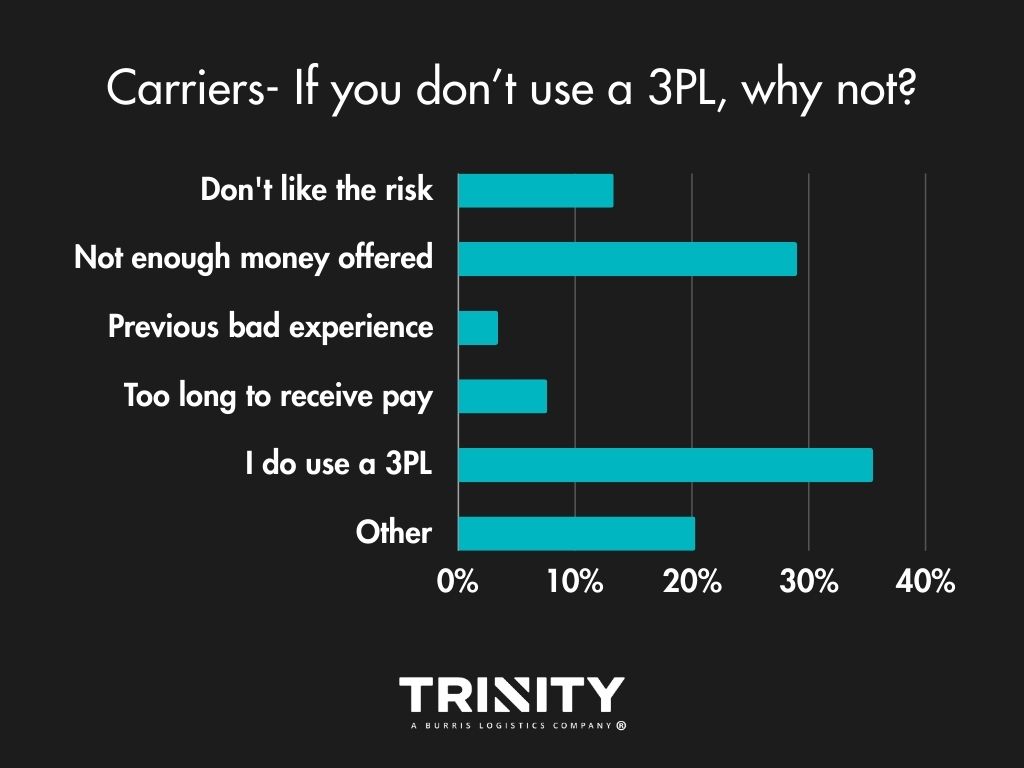
For those that choose to not work with a 3PL, it’s often because of money; rates not being high enough. Surprisingly in the comments, many are not familiar with what a 3PL or freight broker is as well.
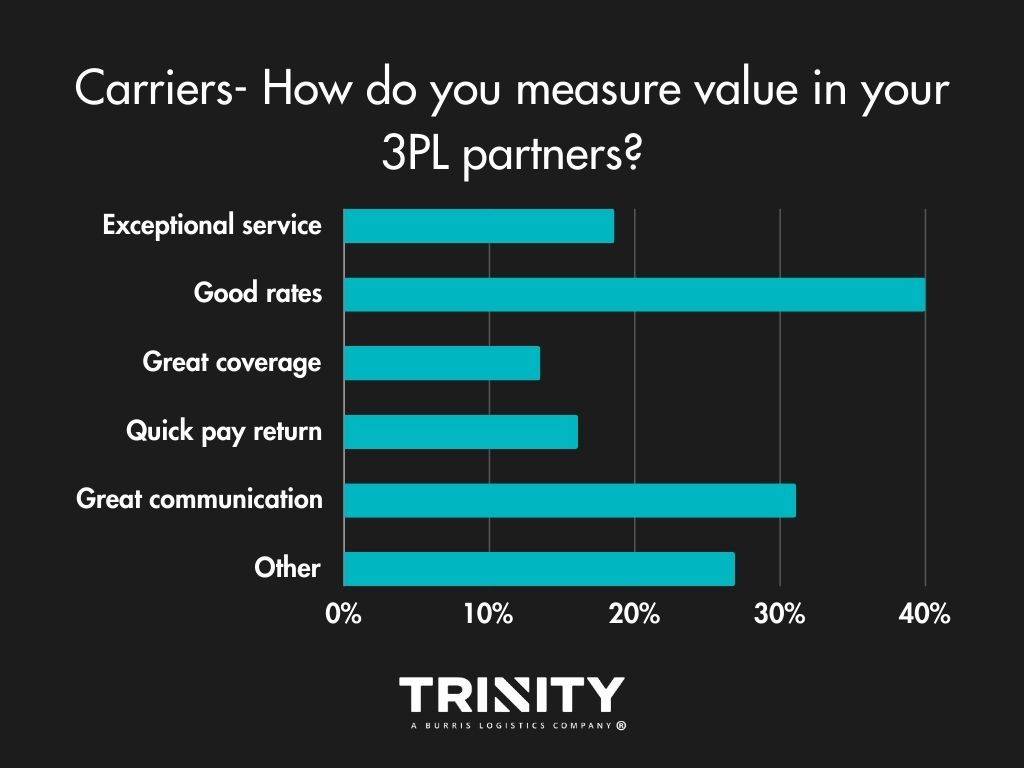
When it comes to measuring value in their 3PL partners, most carriers want good rates and great communication.
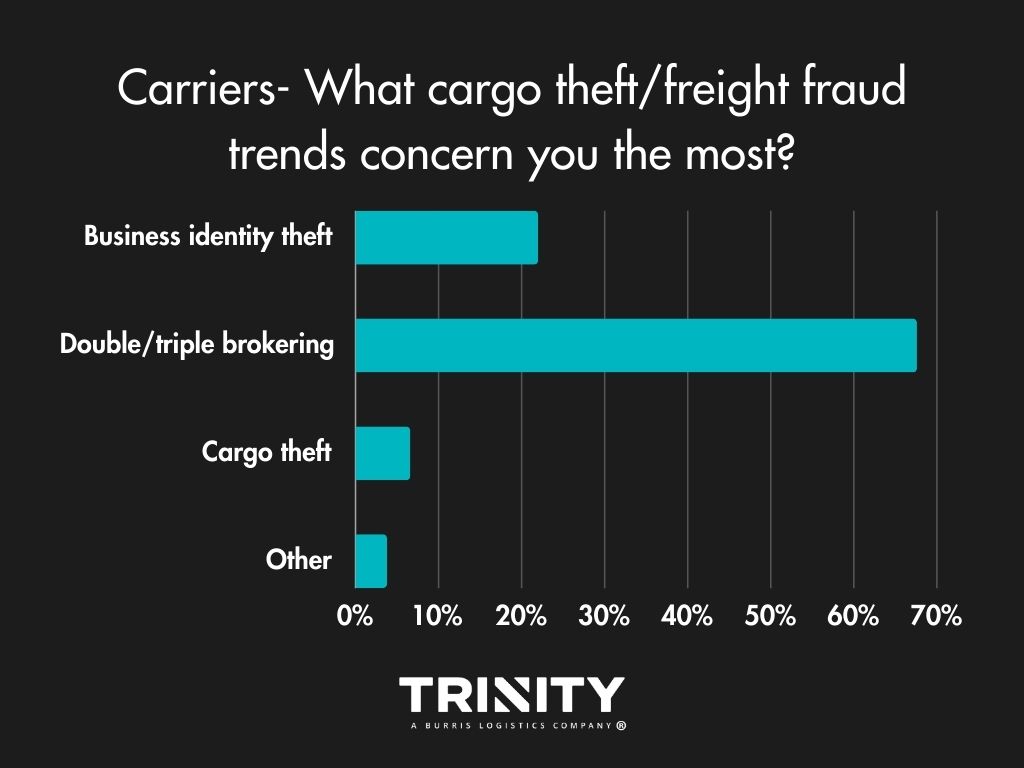
Fraud Concerns Growing
Fraud and scams have been growing in the industry, so we wanted to know what carriers think about it. Carriers are most worried about double and triple brokering affecting their businesses compared to concerns of identity theft or cargo theft.
Stay up to date on the latest information on conditions impacting the freight market, curated by Trinity Logistics through our Freightwaves Sonar subscription.
COULD WE LOSE CARRIER CAPACITY….WITHOUT LOSING ACTUAL CAPACITY?
Certainly, this question could cause one to scratch his head. If we don’t have a decline in the number of operating authorities, or available trucks, then how could we lose capacity?
Well, technically, the answer is you would not be physically losing trucks. However, an impact could be felt from recent events with regards to container shipping that would make it feel like less trucks are available. With recent geo-political events, and events at home, shipping to the West Coast has become more feasible than it was a year, certainly two years, ago. As ocean carriers are mindful of events in the Red Sea, combined with an easing of labor tensions at the West Coast ports, freight that in prior years was diverted to the East Coast is now heading back to the left coast of our country.
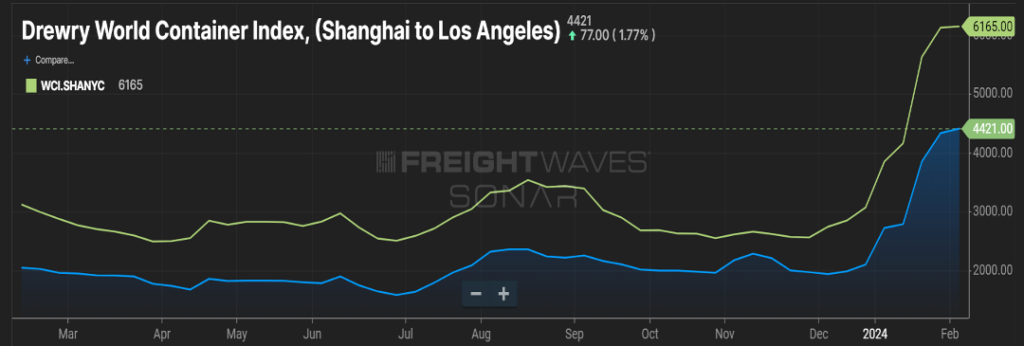
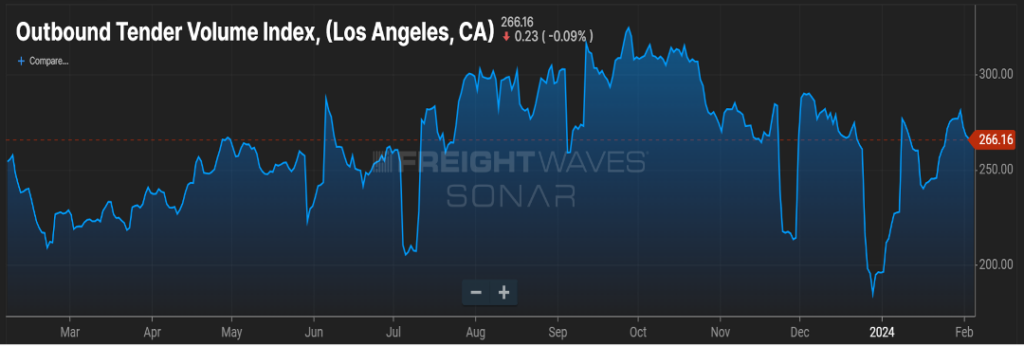
As you can see in Figure 1.1, container costs from Asia to Los Angeles are over $1700 cheaper than freight bound for an East Coast port, such as New York. Figure 2.1 shows outbound freight volume for the last year in the Los Angeles market, currently seven percent higher than this time last year.
So how could this impact capacity? When freight hits the East Coast ports, it’s typically consumed close to the port or at the very least, the coast itself. This means more regional runs. When freight hits the West Coast, typically that freight is destined for locations such as Dallas, TX or Chicago, IL, so taking freight up and down the East Coast may be a one-day run. Freight out of the Los Angeles market, heading to further destinations would take a day and a half, two days.
Same freight, same one-truck move, but now it occupies that truck for twice as long. Additionally, this could necessitate a shifting of fleet resources from one coast to the other, potentially creating an over-capacity on one side of the U.S. while the other coast is more desperate for trucks.
SPRING IN 6 WEEKS?
Will that rodent in Pennsylvania be right this year, and will freight volumes accelerate quicker as a result? First of all, ‘ol Punxsutawney Phil is batting less than 50 percent for his career and the last 10 years he’s only been accurate three times.
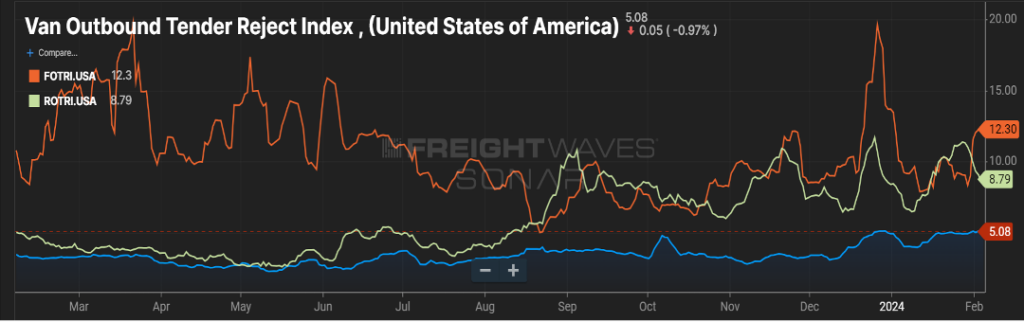
A better canary in the cave would be how the rejection rate index ebbs and flows. As you can see in Figure 3.1, van rejection rates have been pretty stagnant for the past year. Flatbed has remained relatively high and reefer rejection rates have trended up the last five months. If Phil is a soothsayer this year, we expect flatbed rejection rates to continue rising. If produce season also starts earlier than most, reefer rejection rates will then follow.
As reminder, with increases in rejection rates, shippers typically see transportation costs increase on the spot market.
Stay tuned for next month’s update to see if an early spring is a turning of the tide for the freight market.
Stay Up To dAte
Looking for a more frequent update? Subscribe to our newsletter and receive the top five logistics articles of the week every Friday morning by selecting “Weekly News Update” when you select your preferences.
Get Weekly News Updates in Your Inbox